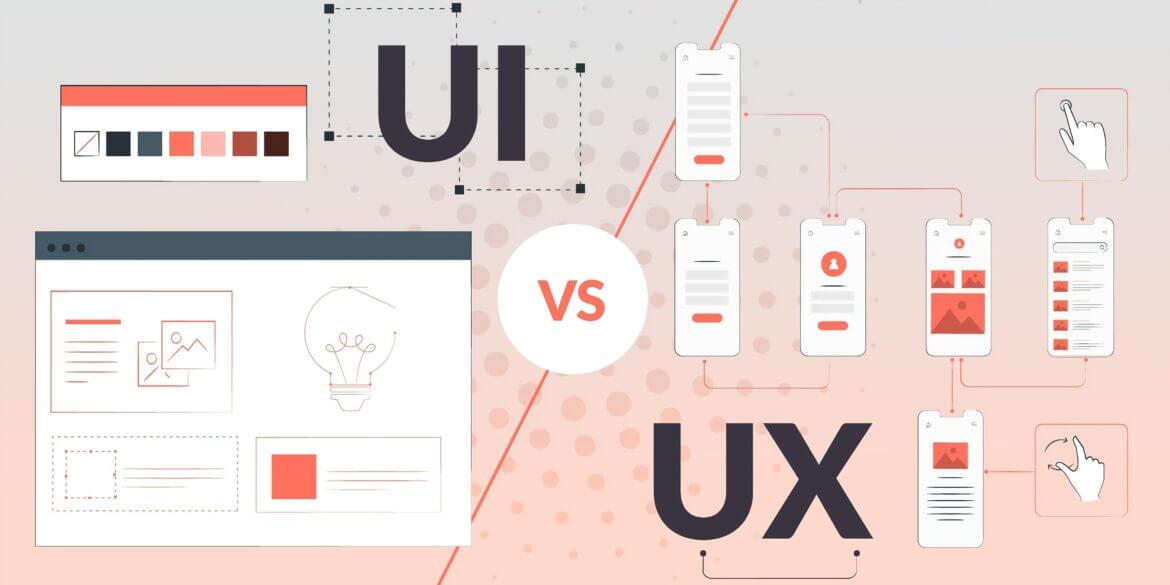
UI vs. UX is one of the longest-running debates in the industry. People tend to use these terms interchangeably, which always causes problems. Although the use and meaning of these terms may overlap, there is a difference between them, especially when it comes to their implications.
We’ll go together through the meaning of these terms and what the differences are between UI and UX in this article. You might have heard that UX is about User Experience while UI is about User Interface, but if you still don’t understand entirely when each one is used, we’ll clarify this further.
While it might seem that there is a UI vs. UX debate, the two work together closely even though they come from somewhat different backgrounds. While UI design is all about visual appeal, focusing on the look, presentation, and feel of a product, UX design is all about the enjoyment and effectiveness of actually using a product.
It all comes down to what the user sees (UI) vs what the user experiences (UX), and these elements work together when you use software development services. Taking the time to see the differences between UI and UX is an important step on your digital transformation journey.
Boost Engagement Through Tailored UX/UI Design
Designing Impactful Digital Experiences That Foster Connection and Increase Sales
Discover UI/UX DesignSome Analogies to Clarify UI vs. UX
Before we talk about how UX vs. UI designs differ from each other but still work together, let’s get deep inside their meaning.
Try thinking of a coffee shop, restaurant, or bar. When you enter, you see chairs, tables, cutlery, bottles, and more. This is the user interface you are looking at. But then you’ll feel surrounded by other elements like music, ambiance, lighting, an, most importantly, the food or the drink that makes up the user experience. When you leave the restaurant smiling, it’s because you experienced a wonderful UX.
If you’re still confused, worry not. Let’s go through another example of the difference between UI and UX that will enlighten your understanding of these concepts!
Let’s say you’re designing a car. The UX would be the components that make the functionality of the car, such as the steering system, start/stop system, electrical system, AC system, exhaust, and more elements that determine how all the car’s features connect together.
Once the prototype of the car is done, you can start focusing on the interior design (UI). The seats, the materials, the colors, the buttons and touchscreens, the steering wheel, the seatbelts, etc. are how the driver interacts with the car – the UI.
Before we talk about how UI and UX differ from each other but still work together, let’s get deep inside their meaning.
Experience the Power of Custom Software Development
Transformative Software Solutions for Your Business Needs
Explore Custom SoftwareWhat is UI (User Interface)?
UI or User Interface means the particular asset or visual touchpoint that the user interacts with. In a simpler manner, it means anything that a user may interact with while he uses a digital product. We are referring to the look, feel, and interactivity of a digital product every time we are talking about the UI.
The UI design implies creating user interfaces transformed from wireframes, easy to use, and aesthetically delightful. These initial designs are usually created with Figma software. The point of interaction between the digital product and the user is the UI, while the UI design is focused on the interactive elements of the product interface.
It’s like an experience customized through color, typography, spacing, icons, buttons, grids, and navigation bar. Under the UI comes everything that is there on the screen, from keys to audio, and lighting, making the interaction pleasing.
When using interactive features meant to guide users through the interface of an app or website, we talk about UI. In the grand scheme of UX vs. UI design, this is a more technical process that optimizes the interaction between users and digital products or devices.
What is UX (User Experience)?
The UX or User Experience is a human-first procedure for designing digital services and products. Don Norman brought the User Experience term to the design scene in the late 90s when he was working for Apple.
He describes UX this way: “User Experience encompasses all aspects of the end-users interaction with the company, its services, and its products.”
UX is a term with a broader meaning and basically applies to everything that can be experienced, from a website to a mobile app, a coffee machine, or a visit to a bar or restaurant. UX resumes to what the customer experiences and feels when using a digital product’s interface.
As an example, let’s suppose you’re using an e-commerce app. In this situation, the UX depends on the ease of finding and buying a product through that app. If you find difficulties when navigating through the categories, finding the product you’re looking for, and experience troubles while searching the ‘Checkout’ button on the screen, before a complete scroll or you have to guess the right icon on the buttons, it comes down to a bad user experience and the potential customer may never return to buy from the e-commerce app.
The primary goal of UX design is the overall experience when the user interacts with the digital product, by understanding the user’s demands while improving the usability and ease for a nice experience. In fact, you can see the ROI of UX design on products that listen to customer feedback and constantly test the app’s experience for optimal usage.
Mobile App Development for a Competitive Edge
Developing Mobile Apps that Engage Your Customers with Your Brand
Explore Mobile App DevelopmentWhat is the difference between UI and UX?
Dain Miller, a famous web developer, helps us understand the differences between the UI and UX through a great analogy:
Try thinking of riding a horse: the elements that make up the whole riding experience fall under the category of UI. In this example, the stirrups, saddle, and rein make up the UI. UX is the feeling you experience when you’re riding that horse.
All the components that enable the user interaction with a product or service form the UI, while the feeling the user receives while interacting with the products forms the UX.
Key Outcomes
Now that we have a grasp on the basic differences between UI and UX, it’s now time to see how they work together. Even though we always compare UX vs. UI design, it’s important to note that these elements work together to provide a finished product.
Which is first, UI or UX?
This question is often confusing and it might have crossed your mind too. The right answer is that the UX (User Experience) comes first and the UI (User Interface) comes second.
While designing a digital product, think of the UX as the parent and the UI as the child. The parent (UX) carries lots of observations, surveys and research to identify the needs of the target audience, before continuing with the UI design.
Even though UI & UX depend on each other while having to work closely together, UX has a slight advantage. A positive experience for your user is created by a good UX design, as it satisfies the user’s needs. A successful product, like a mobile app or a website, requires a good UX design for customer loyalty and satisfaction. Without a good UX, the user is determined to leave your app/website feeling frustration and bitterness about your services, and your goal is to win clients, not lose them.
So remember that a great digital product starts with a great UX design, and then with a great UI design.
Digital Transformation for Competitive Advantage
Empowering Your Business with Tailored Digital Solutions
Explore Digital TransformationHow Do UI & UX Work Together?
Both UI and UX are essential when it comes to a successful product. So if the product looks great but performs badly, this translates into having a great UI and poor UX. If the product has a great usability but looks awful, this translates into having a great UX but poor UI.
You need to find the right balance between these two. UI and UX work hand in hand. How something looks or feels (UI) plays an important role in the overall user experience (UX).
We hope you now have a clear understanding of the difference between UI and UX, and their differences. Just recall that UI is all about the look & feel of the digital product, while UX is all about the user’s overall experience with the digital product.
At the end of the day, it shouldn’t be a question of UI vs. UX. It should be that UI & UX complement one another and go hand in hand despite being vastly different. To see UI vs. UX in action, read about our UX ecommerce experience with Magento.
At HyperSense Software, we work with some of the best UI/UX experts and visual designers in our team, passionate about designing human-centric, responsive and interactive mobile & web apps to provide you a superior design experience. Contact us to find out more about what we do and how we can help you!