Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing various aspects of our society, from job addition to improving customer experience. Yet issues arise as AI progresses. The users’ identity on the internet and the spread of misinformation are among the primary ones. Artificial intelligence can make automated phone calls or replicate online profiles in impossible ways. This ability to fake real persons brings more skepticism about the authenticity of online interactions, making it harder to trust what we see and who we engage with on the internet.
Discover Our AI Integration Experts
Elevate Your Business with Advanced AI Integration Services
Access AI Integration SolutionsWith the continuous involvement of AI bots, it will become difficult to distinguish between human and machine work. This has increased the need for methods to differentiate between human users and other AI-driven bots. A revolutionary idea championed by institutions such as MIT spotlights personhood credentials as a promising idea for positively transforming this scenario.
This article discusses and reflects on the role of personhood credentials and the significance of their impact on individual identity confirmation in the digitalized context.
What Are Personhood Credentials?
Personhood credentials are a reliable and rather sensitive method of confirming that a particular individual is indeed human without sharing too much information on this subject. These differ from traditional identity proofing techniques, which entail using personal details such as names, residential addresses, or identification numbers. Such identifiers do not disclose the user’s personal details and, thus, do not violate their privacy despite operating in settings where identity confirmation is paramount.
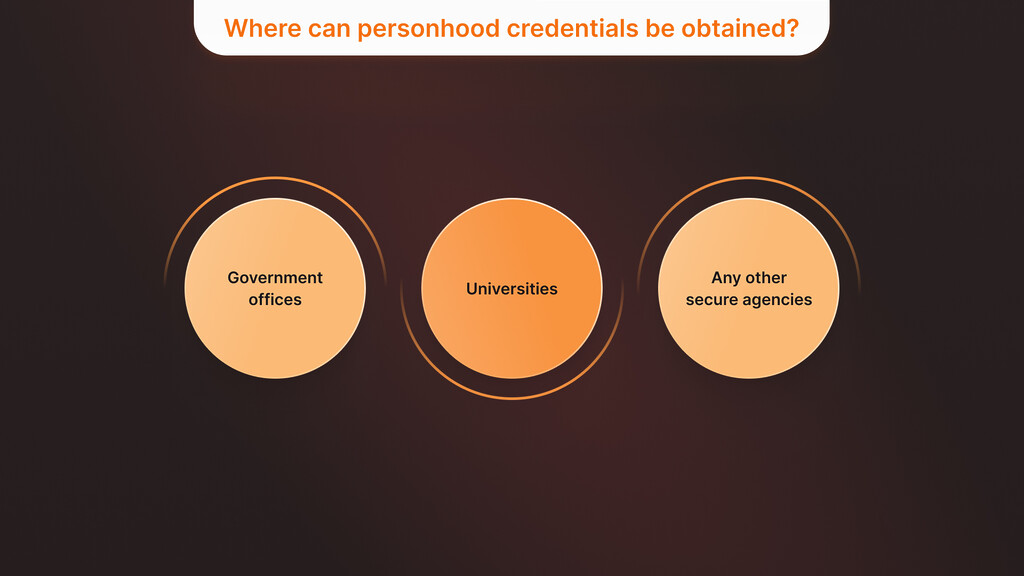
Personhood credentials can be obtained from reliable authorities like government offices, universities, or any other secure agencies and then accepted by the various sites where one needs to use an account. By acting as a verifiable identity of one’s personhood, these credentials facilitate integrated and credible online engagement forms, such as voting in cyber elections, financial dealings, and discussions in any forum, including social networks. To obtain a personhood credential, one must show up in person or have a relationship with the government, like a tax ID number. This ensures the credential is secure and trustworthy.
Making Product Discovery Clear and Accessible
Transform Concepts into Products in Four Weeks with Our Proven TechBoost Program
See Product Discovery ServicesThus, they contribute to retaining the identity and security of digital spaces, which is the foundation for the relationships that occur through computers and the internet.
Technical Basis
As previously mentioned, personhood credentials are built on rather complex technological principles concerning cryptography. They ensure that the credentials cannot be counterfeited or bypassed, not even by the most sophisticated AI systems. Here’s how they work:
Cryptographic Proofs
To assert humanity, personhood credentials rely on non-interoperable cryptographic proofs, such as zero-knowledge proofs. Zero-knowledge proofs enable one party to convince the other that they know some value, for example, a secret key, without the latter revealing it. This serves to prevent the compromising of users’ privacy while at the same time preventing fraudsters from gaining unauthorized access to the system.
Biometric Data
In some realizations, personhood credentials may include fingerprints and face and voice recognition. However, this data is encrypted and stored safely to prevent others from accessing it inappropriately or without permission.
Behavioral Analysis
Behavioral analysis can provide one more layer. This is done by observing and analyzing the activity and interaction of the users, for example, typing style or mouse movement, to distinguish the real users from the bots. These behavioral traits are unique for every user and cannot be imitated by an AI in the same way a human does.
Nouran Soliman, an electrical engineering and computer science graduate student, highlights that these credentials could be used to filter and moderate content on social media, determining the trust level of information received online. This approach aims to protect against AI-driven threats while preserving user privacy.
Custom Software Development for a Competitive Edge
Build Unique Software Solutions with Our Expertise
Explore Custom SoftwareDecentralized Verification
To promote increased security and trust among individuals, the data offered as proofs of an individual’s personhood credentials can be validated using decentralized validators such as the blockchain network. This is important to avoid a single party giving out the verification process, and what could occur may not be genuine.
Privacy-Preserving Nature
Another benefit of personhood credentials is that, unlike most permissions, they respect user privacy. Conventional identity verification processes often involve inputting large sets of highly sensitive data that are hackable and exploitable. On the other hand, personhood credentials are meant to maximize the protection of users’ privacy since they only provide small snippets of data during credentialing.
- Minimal Data Disclosure: The user needs to provide enough evidence to justify that he or she is not a robot. This lowers the odds of personal data being leaked or misused.
- Anonymity: These personhood credentials can be designed to support anonymous interaction while enabling users to prove that they are not bots. This is particularly helpful in situations where the identification of a person is important, such as on discussion boards or voting machines.
- Secure Storage: Any data used in the verification process is stored using the same security measures, so it cannot be accessed by anyone not authorized to do so.
Why Are Personhood Credentials Needed?
The digital environment is gradually evolving; thus, new issues arise, mainly due to advances in artificial intelligence (AI). With the development of AI, the dangers of misinformation, hacking, and manipulation through social media platforms have become more acute. While individuals may remain capable of recognizing fake accounts posted on social media platforms, the risk of counterfeit endorsements from actual accounts has become extremely high. This is where personhood credentials come into play, bringing the much-needed solution to this rising issue.
Threats from AI

AI can reproduce realistic human-like content at a scale previously unknown in the history of humanity. While deepfake videos alter real videos, artificially intelligent generated messages that spread fake news are ways this technology is being used maliciously, affecting trust in cyberspace. Although AI is a powerful tool for delivering messages to audiences, social media platforms have become a popular venue for disinformation campaigns. Bots are utilized to sway people’s opinions, produce fake accounts, and share fake news to influence election results, cause social unrest, or spread fake news.
But, it is not only about disinformation. Cybercriminals now employ bots driven by artificial intelligence in their attacks, like phishing campaigns that use a human-like talking style. These attacks are proving more challenging to detect by traditional security systems, as AI can change its strategy as it unfolds, making more changes. In this environment, it is increasingly difficult for entities, individuals, and governments to discern if they are dealing with a real person, a bot, or an AI system.
When one cannot verify that the participant of an online conversation is indeed an actual human being, the reliability of such environments becomes questionable. From ensuring that the right person gets elected to secure online banking payments or even interacting on social media, personhood credentials are crucial in a world where AI can mimic a human.
Inadequacy of Existing Solutions
Traditional CAPTCHAs were initially effective at differentiating between bots and human users by presenting challenges such as recognizing distorted text or identifying objects in images. However, modern AI systems have become increasingly sophisticated at solving these challenges. Many AI models can now solve traditional CAPTCHA tests with high accuracy rates – sometimes even outperforming humans in terms of speed and success rate.
This has led to an ongoing evolution in CAPTCHA technology, with newer versions incorporating more complex challenges and behavioral analysis. However, even these advanced CAPTCHAs face growing challenges as AI technology continues to improve. Some AI systems can now analyze patterns, process images, and complete interactive challenges in ways that closely mimic human behavior. This advancement has created a constant race between CAPTCHA developers and AI capabilities, making it increasingly difficult to rely solely on CAPTCHA systems for human verification.
While CAPTCHAs still serve a role in basic bot prevention, they are no longer sufficient as a standalone solution for definitively proving human identity in high-security contexts. This limitation has contributed to the need for more robust solutions like personhood credentials, which rely on cryptographic proofs rather than behavioral challenges.
Likewise, anomaly detection systems that identify possible threats by observing outliers or fluctuations in normal user activities are also becoming obsolete in AI. Sophisticated cyber threats that employ AI technologies are nearly always indistinguishable from genuine users’ activities. For instance, the features that bots have are the ability to type, move the mouse, click, and even mimic the online behavior of a real human being. This makes it difficult for conventional intrusion detection systems to detect and report all malicious activities in real time.
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is another form of security where the user is asked for a second form of proof of identity. But even this method has drawbacks. It can be targeted to perform phishing attacks to capture 2FA codes or mimic real users, thus reducing the strength of AI.
The Role of Personhood Credentials
In the face of such challenges, personhood credentials contain useful propositions that are hard to come by. In contrast to other approaches based on identifying abnormal situations or providing challenges, personhood credentials employ cryptographic methods to prove to the system that the user is a real human being. It is worth underlining that these credentials cannot be counterfeited or emulated by AI-brewed systems, contrary to other methods that can be easily mimicked.
Regarding the commitment to Robo-ethics and AI’s increasing threats to human infrastructures, personhood credentials can be considered a future-oriented solution to the core problem of identifying a user as a human. These credentials’ cryptographic methods are put in a way that they cannot be easily tampered with, even by an AI. Hence, the person interacting with the system is a human. In addition, personhood credentials ensure digital privacy security while at the same time affirming the status of a person; this removes the need for users to disclose personal details when procuring personhood credentials.
How Personhood Credentials Work
Personhood credentials are anchored on security principles and prove the humanity that a user can assert without infringing on their privacy. These credentials utilize offline and online processes to provide a strong-proof system free from fraud and easily adaptable to various applications. At the same time, these credentials are built so that the user can have full anonymity with their information while proving that they are human.
Implementation and Issuance
Consequently, the process of obtaining personhood credentials requires several steps to ensure that they are hack-proof and efficient.
Offline Verification
To achieve personhood credibility, a user may be required to go through a form of offline authentication. This usually means going to a recognized facility, such as a government agency, where one can demonstrate in one way or another that they are human. In this process, the user may be required to provide documents proving his identity and complete the biometric examination, for example, fingerprints or a photograph. This step is taken to avoid crediting the fake accounts and the credentials to the real account holder.
Credential Issuance
Upon the actualization of the offline verification, the user is awarded a digital personhood credential. Note that this credential is stored locally in the user’s device, for example, a sophisticated smartphone or a hardware token. It only consists of non-privacy-sensitive cryptographic proofs that facilitate the certification that the user is a human being without divulging their details.
Redefine Your IT Strategy with Our Consultancy
Customized Solutions for Optimal Performance
Discover IT ConsultingOptional Usage
The key characteristic of personhood credentialing is that the users can decide at what point and how they wish to present this credential. Namely, the credentials may be used to gain access to specific internet services, for online voting purposes, or to identify oneself on social networks. This option lets the users own their digital persona, and it is only used where necessary, depending on the credential.
Privacy Protection
Another benefit of personhood credentials is that they can be used to enhance users’ privacy. Here’s how they achieve this:
Isolation of Personal Information
Personhood credentials are mainly developed to maintain the separation of information about an individual. They only take the smallest amount of data needed to verify the user’s humanity during the process. All these data are encrypted, and their storage is protected, meaning only authorized individuals can access them.
Anonymity
The credentials provide a way for users to assert they are human, yet the authentication information is not divulged. This means that it is possible for users to enhance their anonymity while at the same time proving that they are real people. This is especially true where identity is not as important as other conditions are required, such as in voting systems or forums.
Privacy-Preserving Technologies
Personhood credentials build upon complex blockchain features, including zero-knowledge proofs, to ascertain the user’s humanity. Zero-knowledge proofs provide information that enables one party to convince another that he knows a specific value (for instance, a secret key) without disclosing the particular value. This makes the verification process more secure and private to everyone else.
Decentralized Verification
Personhood credentials can be authenticated using decentralized networks, such as blockchain technology, for security and trust. This ensures that none of the entities under the system controls the verification process, significantly minimizing fraud cases.
Potential Benefits of Personhood Credentials
Personhood credentials provide a variety of advantages, which, when used, can significantly improve the safety of online transactions or communication. Here are some of the key benefits:
Enhanced Trust Online
Personhood credentials may contribute to shifting the Internet environment for the better by proving that the people behind it are genuine and not computers. This is particularly important in scenarios involving transactions or sensitive communications, such as:
- E-commerce: Personhood credentials indicate that buyers’ and sellers’ identification can be effectively validated on online shopping sites, thereby minimizing the possibility of fake transactions. This could, in turn, increase consumer traffic in the stores and, therefore, sales.
- Social Media: Personhood credentials can solve all these issues by being used in social media platforms where people create accounts with their details and are validated. This can also improve the quality of conversation shared within social media, making it a safer and more credible platform for users.
- Online Voting: In most advanced electronic voting systems, credentials of personhood can help eliminate cases of vote fraud, as only deserving voters are allowed to vote. This is essential to sustain the integrity of the democratic system in society.
- Financial Services: Personhood credentials also ensure that customers of banking and financial organizations have a genuine, authenticated, and well-recognized identity, hence decreasing the chances of identity theft and fraud. This can expand to more secure online banking transactions and other financial transactions.
Digital Identity Security
As mentioned, using personhood credentials allows users to prove their humanity without revealing personal information. Cryptographic techniques like zero-knowledge proof enable users to identify themselves in a safe and secure environment. Any data used in the verification process is encrypted and stored securely, ensuring that unauthorized parties cannot access it. This reduces the risk of data breaches and ensures that user’s personal information remains protected.
Reduced Misinformation
Personhood credentials may help minimize misconceptions and fake news by making it hard for impersonators to claim fake identities while posting their content. This is especially true with social media and news applications, where fake news can go viral in minutes.
Improved User Experience
Simply, personhood credentials make users’ internet experience more private and smooth. For instance, they can sign into many services with many accounts and different passwords for each account since the personhood credential proves who the person is.
Risks and Challenges of Personhood Credentials
Although this paper argues that personhood credentials are beneficial in providing enhanced security and privacy, they come with numerous risks and challenges, as discussed above. These issues mainly focus on the power of issuing entities and the possibility of some persons’ exclusion due to accessibility issues.
Concentration of Power
Arguably, one of the most significant precursors to concerns about the feasibility of personhood credentials is the conflict of power, where there may arise a single central authority or monopolistic set of institutions that oversees the issuing of the credentials. When personhood credentials are in the hands of governments, corporations, or specific institutions, the issue of how much control they have over our digital identities arises.
Trust Issues
This could lead to a situation where the issuer of credentials becomes a controller of digital access, fixing who gets which credentials and at what standards. Such centralization may also cause problems such as a lack of trust or confidence, particularly if the central authority institution is corrupt. The users may also have doubts about the bias of the issuing organization, whether the organization is politically or socially biased in any way. Furthermore, centralizing the issuance of personhood credentials may also result in some unhealthy vices, such as misuse or abuse of the power in issuing the personhood credentials. However, the governments of authoritarian states might use this system as a means to manipulate or spy on their citizens, thus overstepping the measures that protect people’s privacy.
Misuse of Power
In relatively more democratic contexts, a similar over-arching authority would exist that has been delegated the power to grant personhood credentials, and similar power would have to be accountable to resist abuses – for example, refusing to grant credentials to individuals of certain characteristics or rigging the system to favor some groups. The power to influence the masses has to be used with lots of responsibility and precautions, such as overpowering any group or parties to gain undue advantage, as this will build a system of distrust that will be counterproductive in the long run.
Decentralized System
The identified challenge shows that one solution is to use a decentralized system in which several competent institutions act as issuers and verifiers of personhood credentials. This would assist in decentralizing power relations and decrease the probability of a single organization dominating the process. Furthermore, decentralization may enhance users’ confidence since the system would not be vulnerable to the authority’s control.
Accessibility Issues
There is still the problem of access, which also arises because the holders of personhood credentials cannot necessarily go to the issuing institutions to get their credentials. Since many credential systems of personhood may involve an offline authentication process, for example, going to a government office or an accredited institution, this could hinder people living in rural areas or areas with little development.
In some countries with politically unstable or dictatorial political systems, some categories of the population may be intentionally deprived of obtaining such credentials due to political, ethnic, or social hostility. For instance, the members of any minority group may face challenges in reaching the government offices or any other verification centers. Thus, they could be denied access to personhood and participate in the digital environment, which presupposes personhood qualifications and enhances the existing inequality and digital dives.
Likewise, social and economic constraints make obtaining or paying for personhood credentials difficult for some. It could prove quite challenging for those who do not have appropriate ID documentation, for example, refugees, undocumented individuals, or those who have been forced to abandon their documents for one reason or another. Also, to get to verification sites, users could incur other expenses such as transport, time, or monetary charges, which may be regarded as a burden for those in the low-income category.
In response to these accessibility concerns, it will be significant for personhood credential systems to incorporate other authentication methods that are not pasted on physical presence in credential-issuing sites. This could be through using mobile phones, conducting verification via the internet, or incorporating local institutions to increase the reach of personhood credentialing to as many people as possible. Furthermore, a distributed system in which different institutions can award credentials can be an advantage, make the system’s accessibility more widespread, and increase the number of people who can enroll through various channels.
Future Outlook and Next Steps
Need for Regulation
AI technologies are evolving at an alarming rate. Therefore, it becomes crucial for governments and technology firms to work together to issue standards for credentialed personhood before AI dominates current security solutions. As the threats involving AI progress, including deepfakes, disinformation, or cyberattacks, become more complex, a clear and integrated legal framework will be necessary to guarantee that personhood credentials are used securely.
Advanced R&D Solutions Tailored for Your Business Growth
Innovation Is at the Core of Every Product Through R&D-Focused Software Development
Learn About R&D ServicesIt is about time governments joined forces with technology giants to establish best practices or policy guidelines on how and when such credentials are awarded and governed, how they are secured from misappropriation, and how all this can be done privately. This way, trusted domains would be surpassed by AI. Thus, it becomes too challenging to maintain security and confidence in online environments due to a lack of proactive regulation.
Broader Adoption
Replacing the current Global Personhood Credentials system implies involving researchers and policymakers in the discussion to unite under the common goal of advertising this technology for the security and presumed liberty of the world. Such credentialing has to be done cautiously to let people demonstrate their humanity and, at the same time, maintain their right to privacy or freedom of speech).
While socially valuable and valid reasons exist to construct more sophisticated, large-scale verifiers of personhood, its lawmakers guarantee that such systems are maximally equitable, inclusive, and positivist. Introducing international collaboration will be crucial because wider usage by various industries and countries will contribute to developing secure environments that would enable real and safe digital communication. Ethical considerations can, therefore, be used by personhood credentials to attain trust without cost to civil liberties.
Empowering the Future: Building Trust and Security in the Digital Age
Consequently, personhood credentials can be considered a significant step forward in the probative value of identity documents. Using cryptographic methods and privacy-enhancing technologies, they offer a reliable and low-entry approach to producing proof that, indeed, you are a human being while at the same time preserving privacy. This makes them a valuable tool to curb the high fraud and identity theft rates, especially in the cyber world, making it a safer arena to conduct business.If you want to use cutting-edge digital identity solutions like personhood credentials, contact us for a customized and reliable solution tailored to your business.
What is meant by “Personhood Credentials”?
Personhood Credentials are alphanumeric strings that prove a person is a human, not a machine. They can be used to log in to online platforms and services with security assurance.
What is the idea behind Personhood Credentials?
Personhood Credentials depend on cryptographic structures that AI systems cannot overcome. To get these credentials, a person has to prove that he is human by physically going to an issuer, like the government or any other trusted organization.
What is the significance of the use of Personhood Credentials?
They help avoid the abuse of AI by allowing only people’s abilities to access specific services on the internet. This can help minimize the spread of fake news, spam, and other malicious actions bots perform.
What organization is eligible to provide Personhood Credentials?
Only trusted governments and organizations can provide Personhood Credentials. Such issuers confirm an individual as a human through physical presence and other strong authentication procedures.
Are Personhood Credentials safe?
Yes, they are designed to be secure, and the privacy of the data is highly guaranteed. The credentials use the best cryptographic mechanisms to avoid the possibility of forging or misuse by artificial intelligence systems.
Will Personhood Credentials affect my privacy in any way?
No, the reason for having Personhood Credentials is that they are supposed to demonstrate that you are a person without disclosing other details about yourself. They offer confidentiality while at the same time providing the right authentication.
What do I need to do to be issued with the Personhood Credentials?
To get the Personhood Credentials, you had to go to an authorized issuer in person. The issuer will check your humanity and issue you the credentials.
Are the Personhood Credentials applicable in any part of the globe?
Yes, the intention is to have the Personhood Credentials accepted and utilized internationally to prove one’s humanity in different online platforms and services.
Are personhood credentials legally recognized today?
Not yet in the majority of jurisdictions. Nevertheless, governments and standards bodies are pursuing regulatory frameworks to acknowledge and regulate such credentials, particularly amid the growing threat of AI.
How do personhood credentials align with data protection laws such as GDPR?
Due to the lack of storage and disclosure of personal details, the use of personhood credentials may be more privacy-conscious than other traditionally used IDs and aligns more closely with the principles of GDPR.
Do personhood credentials work offline or in low-connectivity areas?
Yes. Credential storage may be performed on the device and used in offline mode, with verification again when the device becomes available.
Are personhood credentials resistant to future AI or quantum attacks?
The majority of systems are based on post-quantum cryptography, such as zero-knowledge proofs, and are expected to evolve as post-quantum security requirements become more stringent. Audits and regular updates are guaranteed to provide long-term resilience.
How can businesses integrate personhood verification into their platforms?
The majority of systems are based on post-quantum cryptography, such as zero-knowledge proofs, and are expected to evolve as post-quantum security requirements become more stringent. Audits and regular updates are guaranteed to provide long-term resilience.