Data lakes let businesses pour in every byte of information—web clicks, sales transactions, customer-service chats, IoT sensor streams, social posts—exactly as it’s generated, without first sorting or schematizing it. By storing raw data in one scalable, low-cost reservoir, leaders can postpone modeling decisions until analysis is needed, giving analysts, data scientists, and AI systems instant access to the freshest, most complete picture of the business.
What Is a Data Lake?
A data lake is a large area where data is stored. You may consider it a place where all your company’s essential data is stored. You do not need to modify or update the details from sales, the web, mobile apps, customer service, sensors, or social networks before they are fed into the system. Data stored in a data lake has not been altered or sorted. You can use Excel data or extracts from databases to discover videos, PDFs, and even raw logs. This type of database differs from a typical one, as it doesn’t require all the information to be stored in tables. At the same time, data lakes store data without first organizing it.
This approach is helpful because it allows you to record small and important details you might miss with a specific format. A professional explains that, in a data lake, all original data remains unchanged until users decide what to do with it. In other words, your IT team can collect current data today, ready for use in any upcoming scenarios. If the analyst needs something from the lake, they can use the raw data to update or make the required reports or models immediately.
Using big data tools like Apache Hadoop, Amazon S3, Azure Data Lake Storage and Google Cloud Storage is how data lakes are normally built. Such platforms offer users the option to save various types of data.
Your Path to Innovation Starts with Digital Transformation
Customized Digital Strategies for Competitive Advantage
Explore Digital Transformation- Relational data that is found in transactional systems
- IoT devices generate logs and telemetry.
- Words, pictures, and videos are all types of content.
- Files in JSON, XML, and CSV formats
The use of the right infrastructure allows businesses to do analytics and machine learning on the lake without having to move or duplicate data.
To understand how data lakes can handle large-scale scientific data, check out Harnessing HPC and Cloud Pipelines to Tame the Genomic Data Deluge from the HyperSense blog.
How Data Lakes Work
Data lakes are often constructed with highly scalable storage, allowing them to expand as your data grows. The lake is always receiving data from the various systems. You can consolidate your web server logs, data from your CRM, marketing information, financial records, feeds from IoT devices, and social media posts into a single data lake. It is important to note that, with this system, the data is simply read and not changed at all ahead of its use. It is only after analysis that someone uses a structure to answer a particular question.
With data in the lake, each team in your organization can work with it using their preferred tools. A data scientist could link Python or Spark to observe patterns in data and train machine learning models. Business analysts can use SQL queries or create visualization dashboards. Since the lake has the source data, it can be applied to various analytics and AI projects. A team can extract web statistics and customer comments from the lake to spot new trends. The finance team could also utilize the lake to query sales data and determine how the company performed during each quarter. Everyone accessing the system can use the same data, without having to copy or transfer anything.
All in all, a data lake provides a flexible place for your data to gather before being processed. It accepts any amount of data from any source immediately and stores it for a short period while it is not in use. When analysis is required, data can be modified, combined, and transmitted to dashboards, reports, or AI for additional processing. For this reason, data lakes are an important part of current data architecture solutions.
Benefits of Data Lakes for Business
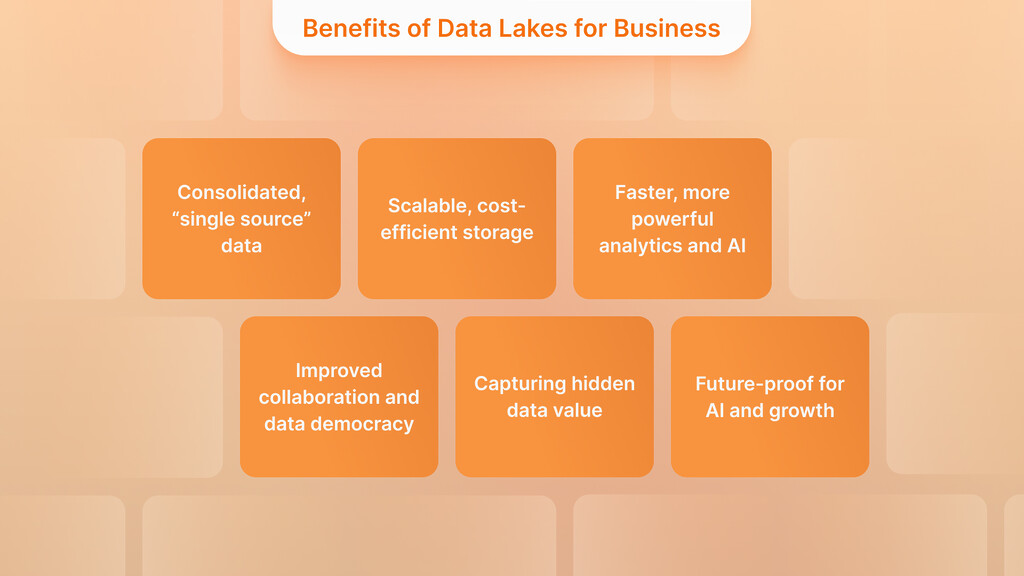
The critical question for business leaders is this: How valuable is a data lake? The reason is that it enables you to utilize your data more effectively and make more informed decisions. Let’s discuss the main benefits a data lake can offer to a business:
- Consolidated, “single source” data: When every important piece of information is put in the same data lake, information is shared more easily. The source also notes that by collecting data in a lake, information becomes accessible to all departments in one centralized location, enabling them to share insights with one another.
- Scalable, cost-efficient storage: With data lakes, companies can store vast amounts of data at a low price. Paying for storage is the only expense, as all the data comes in the same format. In other words, you can manage a vast amount of data without needing too much money. For instance, Netflix uses data lakes to preserve a lot of raw information about users’ behavior. Because of this approach, they can put data in any form and use analytics and personalization without first cleaning it. Simply put, with a data lake, you can collect more data since you are confident it will be helpful in the future.
- Faster, more powerful analytics and AI: You can analyze live information using data lakes or use the data as the base for advanced analytics or machine learning. For example, it is noted that with the collection of vast amounts of data, corporations can utilize current methods to gain instant insights and inform their decisions. Consider that Tesla collects live vehicle data into a data lake to enhance performance and prepare for maintenance. Just like a data warehouse, a data lake makes it possible for data scientists to use multiple types of extensive data for training AI. An industry expert states that businesses can keep all their data, regardless of the possible future questions they may have. This ensures your analytics tools will not become obsolete.
- Improved collaboration and data democracy: Everybody in the company can use the data in the unified data lake. Rather than having each department keep its own reports, a central lake makes it possible for everyone to use the same data. By doing this, Coca-Cola facilitates easier communication and cooperation among various teams, as they all have access to the same data. In other words, a data lake enables more people to work with data, eliminating the need for specialists to handle it.
- Capturing hidden data value: In many businesses, a lot more unstructured and unused data exists than most realize. According to industry surveys, approximately 80–90% of business data is unstructured, and much of it remains unexamined. A data lake overcomes this by keeping all your text, images, logs, and so on in one place, even before you decide how to use them. You keep the possibility of extracting the value from it in the future. As a result, you save time and money by not cleaning immediately. Instead, you store the sample now and look at it later. Doing so could bring up new ideas – for instance, examining customer service conversations or social media messages might show things that other databases overlook.
- Future-proof for AI and growth: Because every bit of your data is in the data lake, your company is prepared to use AI and data science. Because AI is being used more and more, storing a big pool of data gives companies a decisive advantage. You can try out new machine-learning models on your existing data, without changing your original system. The Salesforce guide points out that data lakes are flexible in holding different types of data and save both time and money by letting you store data without first organizing it. So, they allow your company to see all aspects of its business and customer base, which makes it easier to innovate.
Experience Our Research & Development Expertise
R&D-Led Software Development Integrates Innovation into Every Product Detail
Learn About R&D ServicesA data lake, designed well, can significantly boost a company’s ability to adapt and learn from its data. You can gather all your data now and analyze it later, which helps you move faster from data to business gains.
If your organization is moving to the cloud, don’t miss Cloud Migration: Strategies, Benefits & Common Pitfalls for guidance on avoiding governance issues and data mishandling.
Example: A Data Lake in Action
Let’s think about a retail company that decides to construct a data lake. Their system is set up so that data from all activities, such as web clicks, sales, supply, and customer ratings, is sent in. All this data is automatically added to the lake without any formatting.
Now, assume that the marketing team wants to work on making customers more engaged. Data scientists can examine the data lake to discover how visitors learn about the website (through search, ads, or social media), which pages they review, and which goods they purchase, without having to copy the data first. If they analyze their browsing log and sales data, they could identify a new customer trend (for example, items advertised on social media sell better) and take action by adjusting their stock or advertising efforts. At the same time, the operations team relies on the data lake to identify problems in the supply chain or improve the company’s pricing quickly.
This is not only an idea. Amazon keeps customer data, stock, and sales stats together in a data lake, which means teams can monitor preferences and handle supply chains more efficiently. Netflix collects detailed data about what each user watches and stores it in a data lake to help with their suggestions. Regardless of the case, the data lake consolidates all data in one location, allowing different teams within the business to access and utilize the information more easily.
Data Lakes vs. Data Warehouses
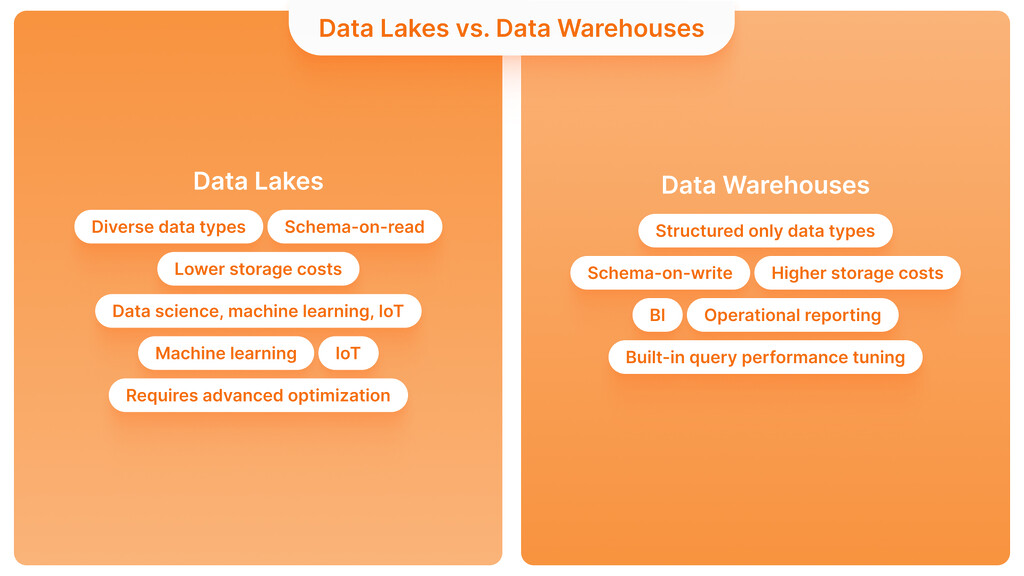
I should mention that a data lake is not identical to a data warehouse – they are used for different reasons. A data warehouse is designed as a reliable structure for reporting and analysis purposes. You should clean and arrange your data before loading it. Unlike a data warehouse, a data lake can accept all kinds of data and organize it afterward.
A good way to picture it is to think of a data lake as a natural lake that collects rainwater – every bit of data can flow in and blend together. Similarly, a data warehouse can only accept data if it is properly ordered and labeled. A warehouse won’t accept a pile of unsorted items; everything must be prepared beforehand. In a similar manner, data lake processes store data and then organize it later, whereas a data warehouse primarily focuses on arranging and structuring data.
In reality, companies often use both strategies. You may want to use a data lake to store all your data, while a warehouse is best suited for generating consistent daily or monthly reports. According to Amazon’s data architects, most organizations find they need a lake and a warehouse, as each serves a different purpose. You could set up your typical BI dashboards (regional sales and inventory status) in a warehouse while doing ad-hoc, AI-based tests or mixing new data sources in a data lake.
It is essential to distinguish between a data lake and a data warehouse when evaluating the necessary data infrastructure. Although they both provide storage, they have distinct architectures, varying levels of flexibility, and different use cases. This difference allows company leaders to pick the right data management system for their needs: operational reporting or deep analysis.
| Feature | Data Lake | Data Warehouse |
| Data Types | Structured, semi-structured, unstructured | Structured only |
| Schema | Schema-on-read | Schema-on-write |
| Storage Costs | Lower (uses commodity hardware) | Higher (optimized for queries) |
| Use Cases | Data science, machine learning, IoT | BI and operational reporting |
| Performance Tuning | Requires advanced optimization | Built-in query performance tuning |
For businesses using AWS, AWS Genomics Data Storage & Cloud Processing Pipelines Guide offers deeper insight into cloud-based processing and storage.
The Strategic Potential of Data Lakes

Data lakes are not only a trendy term for data-driven companies; they are key resources. If all your business’s data is stored in one place, it helps them discover insights you might not see otherwise. Research reveals that companies are noticing the benefits: around 69% of businesses had data lakes in 2021, and the market for data lakes is expected to reach almost $46 billion by 2030.
Building the Future on Liquid Insights
For those leading a business, the primary benefit is that a data lake can organize unstructured data, making it easier to utilize. As a result, companies can act quickly, serve customers individually, predict future actions, and introduce more innovative solutions. When companies fully utilize their data, they often achieve significant results: a study revealed that data-driven leaders improved their ability to acquire and retain customers by nearly 90%.
To make a data lake work effectively, you need to plan well for data governance and security, and the benefits are worth it. The data lake is flexible: as your team requires access to new information or tools, they can utilize the lake without needing to start over. Due to the impact of AI and big data, being flexible provides organizations with a distinct advantage.
Leading AI Solutions for Your Success
Drive Innovation with Our Dedicated AI Integration Services
Access AI Integration SolutionsOverall, data lakes allow your business to collect and save information without knowing its exact future use. It requires being equipped for the next important discovery, regardless of whether it’s found through analysis, machine learning, or a new strategy. With all your data in one place, a data lake allows you to turn raw information into practical value for your company.
To explore integration options that combine data lakes with modern technologies, read AI Integration for Business: Practical Steps to Implement and Scale.
If you are interested in developing a data strategy with custom software, contact us at HyperSense Software for support. We create and deploy systems that scale up, remain secure, and are tailored to meet specific needs, helping data become a strength for companies.
Let’s piece together your business’s future, step by step, using valuable insights.
Key Takeaways
- Data lakes are an economical and adaptable solution for storing and handling large amounts of diverse data.
- These systems differ from data warehouses in their flexibility, setup, and primary tasks.
- Utilizing a cloud strategy can lead to improved data analysis, cost savings, faster insight comprehension, and support for AI and ML.
- Many real-life cases demonstrate that data lakes can enhance the operations of retail, finance, healthcare, and other sectors.
- Specific actions to strengthen security reduce the risk of information leaks.
What is a data lake in simple terms?
A data lake is a centralized repository for massive volumes of raw data from multiple sources, such as CRMs, web applications, Internet of Things devices, and social media. It enables you to store both structured and unstructured data without first formatting it, making it well-suited for future analytics, AI, or reporting.
What is the difference between a data lake and a data warehouse?
A data warehouse is a repository of clean, structured data used for reporting and BI. A data lake contains raw, unstructured, and semi-structured data that lack predefined formats. Machine learning, data science, and ad hoc exploration are more suited to data lakes, whereas dashboards and standardized KPIs are more suited to warehouses.
What are the main benefits of a data lake?
The main advantages are low cost, expandable storage, real-time analytics and AI support, and easy access to any type of data. Data lakes also enable cross-departmental collaboration and store data that can become useful in the future.
Why should I store unstructured data in a data lake?
The raw data, such as PDFs, images, and logs, can be unstructured sources. A data lake allows you to store it there and form it as you go, analyze it later, and avoid losing business opportunities that non-traditional structures might capture.
How does a data lake support real-time analytics and machine learning?
Data lakes receive real-time information. This allows teams to apply machine learning models, run predictive analytics, and create dashboards in real time without requiring data migration or transformation of the underlying data.
Can multiple teams access and use the same data lake?
Yes. An organized data lake provides secure role-based access, enabling marketing, sales, finance, and IT departments to work on the same data without creating silos or duplicates.
What industries use data lakes the most?
The retail, financial, health, and manufacturing industries use data lakes to gain insights into their customers, detect fraud, perform predictive maintenance, and comply with regulatory bodies. Their scalability enables them to fit into any organization with large data volumes.
Which companies use data lakes successfully?
Companies such as Amazon, Netflix, Tesla, and Coca-Cola have embraced data lakes to store user behavior, sales data, video streams, and sensor inputs, enabling personalization, logistics, and real-time decision-making.
What are the most significant data lake challenges and risks?
Without policing, data lakes can become a data swamp. The risks include data leaks, low data quality, and access issues. To prevent this, companies will need to implement encryption, access control, metadata management, and data cataloging.
Do I need both a data lake and a data warehouse?
The two are associated with the benefit of most companies. A data lake is the best place to store raw data and execute AI models, and a warehouse is the best place to perform fast queries and regular business reports. The combination of them offers an overall data strategy.
How do data lakes prepare my business for future AI use?
Data lakes make your company AI-ready by storing raw data at the beginning of the process. You stop having to restructure systems towards the end of the business cycle and train new models, test hypotheses, and adapt more quickly to future business questions.
How do I start building a data lake?
Start with specifying your data objectives, selecting a cloud provider (AWS, Azure or Google Cloud), and deciding how to govern it at the outset. Give usability and long-term value using scalable infrastructure and cross-functional teams.
What tools and technologies are used to build a data lake?
Apache Hadoop, Spark, Amazon S3, Azure Data Lake Storage, and Google Cloud Storage are popular. They provide scalability, support for multiple data formats, and the ability to integrate analytics and AI tools.
How do you secure a data lake and prevent data leaks?
Encryption at rest and in transit, role-based access control (RBAC), audit logs, and governance tools such as AWS Lake Formation or Apache Ranger are necessary to secure a data lake. Such actions deter unauthorized entry and data loss.
What is a data lakehouse, and how is it different?
A data lakehouse is a data warehouse that incorporates data lake characteristics. It supports storing raw data in a lake and adds schema management and ACID transactions, similar to a warehouse. Analytics Lakeshouses help connect analytics and reporting within a single platform.