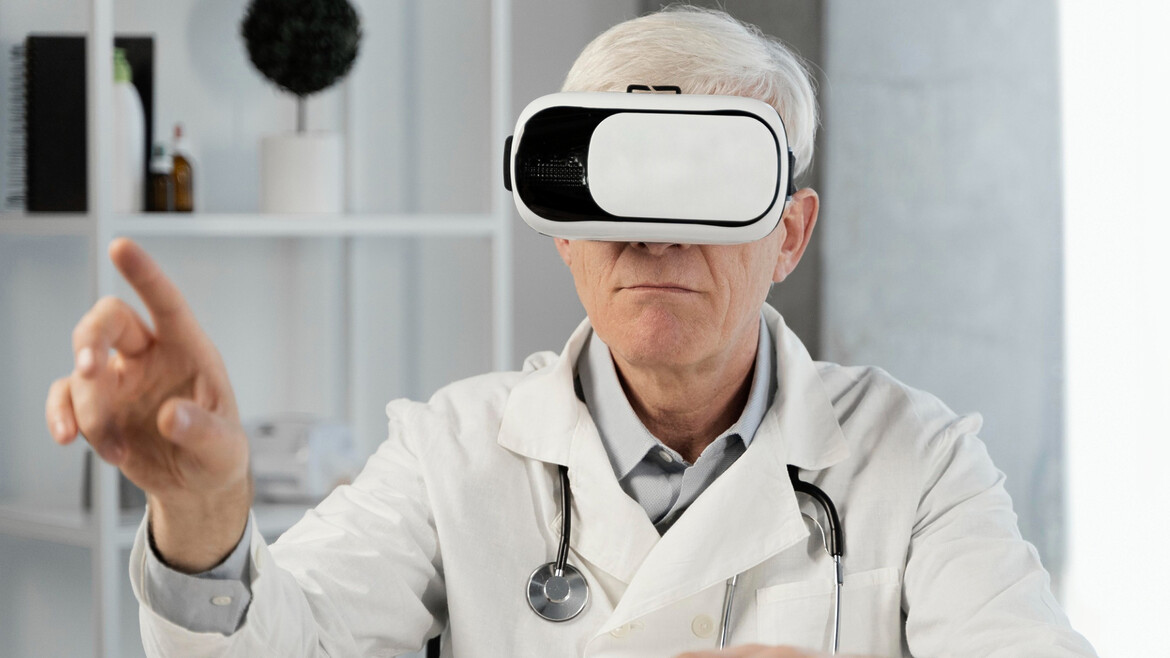
The modern healthcare system has been rapidly growing and developing, and the role of technology in forming healthcare advancements is unearthing a new way of learning, practice, and skill enhancement among medical practitioners. Among these innovations, Virtual Reality in Medical Training is easily one of the most promising. Recognizing how this technology works is crucial for businesses to provide innovative solutions in healthcare education.
This comprehensive guide provides an overview of VR Medical Training, focusing on the strengths, technologies, and numbers that support the idea that now is the right time to embrace Virtual Reality in Medical Education.
Digital Transformation for Competitive Advantage
Empowering Your Business with Tailored Digital Solutions
Explore Digital TransformationThe Growing Demand for VR in Medical Training
This urge to learn high-quality medical education is more profound than ever. As healthcare delivery systems become more expansive and patients’ conditions become more nuanced, there is a need to address patients’ needs due to their complexity adequately; conventional training methods are inadequate. The situations must be as close to life as possible because in a live case, very often, one’s mistake can cause an individual’s death.
Virtual Reality Medical Education helps solve this problem by offering an environment enabling learners and professionals to practice several tasks, get feedback immediately, or mimic some complex and rarer operations. Learning skills in a VR environment, which replicates the real environment, results in better performance in real-life clinical situations.
The worldwide virtual reality market in healthcare was estimated at USD 3.12 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 38.46 billion by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 32%. This growth trend shows the broadening use of VR in medicine use and other related fields of healthcare.
What is Virtual Reality (VR)?
Virtual Reality is an advanced technology in which a virtual environment is built where the user can place himself and experience 3D objects and space. In this case, people use VR headsets and feel physically in such environments, making it suitable for recreating scenarios. In healthcare, the use of VR is changing the training and practice of healthcare providers.
Evolution of VR in Healthcare Education
VR originated in the 1960s and was first used in aircraft pilot training as its primary application, though it has expanded widely in tandem with the enhancement of technology. Initially, VR was employed for simple medical modeling; it is currently used in surgical practice, anatomy, and therapy. Later, by the year 2010, VR was brought to the market, and today, it is essential for developing lifelike scenarios, which are crucial for physicians’ training purposes.
Today, Virtual Reality in Medical Training is essential in preparing healthcare specialists. At first, VR was applied to general clinical learning to demonstrate fundamental video anatomy or elementary operations. However, present-day applications of VR are enhanced by better hardware and software technologies so trainees can conduct complex surgeries or perform emergency responses in virtual reality. Virtual Reality in Medical Training has evolved from a mere practice of orientation to an integrated system of present-day medical training, as it is widely incorporated in universities, hospitals, and other specialized medical facilities.
Why use VR in Medical Training?
For years, medical training has been dominated by classroom learning, prosection, and clinical clerkships. However, these valid methods have major drawbacks, especially when developing professionals for the dynamic and critically demanding healthcare sector.
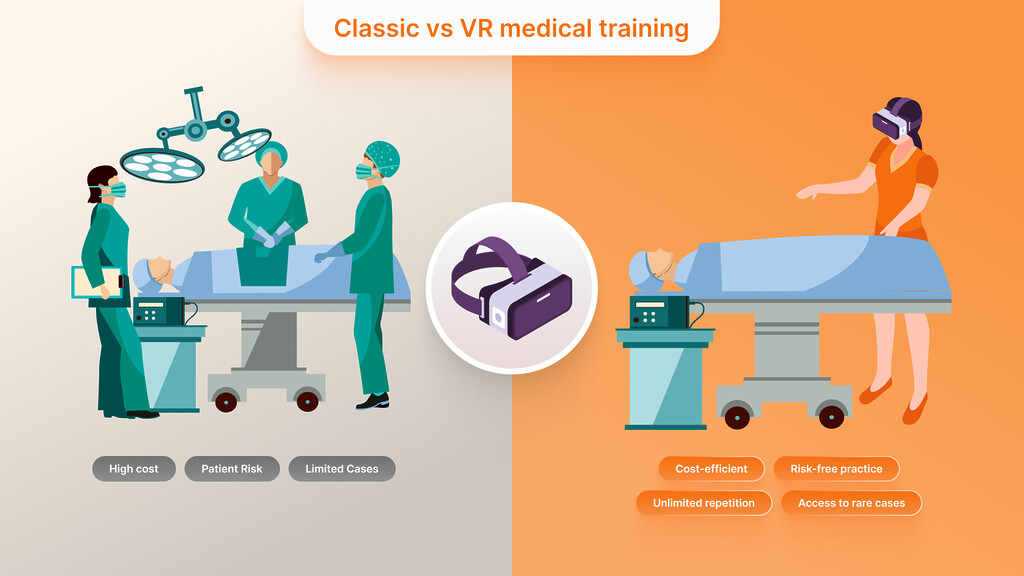
Limitations of Traditional Training
- High Costs: Cadaver dissection and simulation labs have always been expensive training techniques. Operating these facilities costs a lot of money, and therefore, many institutions lack the capacity to fulfill this need by offering elaborate hands-on experience.
- Limited Hands-On Practice: Medical students usually have very few chances to perform certain rare or complex operations. Although actual human bodies are valuable, practicing on a cadaver is different, and in clinical scenarios, students may not be exposed to many different scenarios.
- Risk to Patients: Live patient treatment comes with risks, and students can lose much learning. However, mistakes made during students’ practical education can cost patients’ lives. This risk diminishes the trainees’ ability to perform independently and make mistakes from which they could learn.
How VR Addresses These Issues
Virtual Reality Medical Education addresses these challenges by providing an increasingly convenient, accessible, and safe approach to medical training.
Cost-Efficiency
Generally, once a setup for a VR Medical Training system has been developed, it can be utilized again without going through costly procedures. This makes VR more affordable than other methods that use constant resources like cadavers or costly simulation devices. While developing VR solutions, institutions of different types can equip their learners with the same quality education.
Immersive Learning
Another strength of Medical Training with VR is that it involves creating rather realistic environments. Learners are exposed to real-life situations in three-dimensional settings, including patients, surgical instruments, and emergencies. Such an engagement also provides a better learning experience and enables one to understand anatomy, procedures, and decision-making under pressure.
Risk-Free Practice
Virtual Reality in Medical Training allows students to practice complicated and critical operations without harming the patient’s life. Every mistake is made, discussed, and rectified under controlled conditions, where practice can be made innumerable times until one masters it. This freedom to fail and learn is very important, especially in specializations such as surgical specialties or trauma that require high accuracy.
Access to Rare Cases
A strength of VR is that it can present occasional or challenging scenarios that a trainee might not experience in clerkships. VR’s flexibility means that any aspect of healthcare education, from major operations to emergency call-outs, can be replicated. Thus, learners are exposed to a vast array of possibilities. This preparation is essential in enhancing trainees’ ability to handle various medical endeavors.
Repetition and Feedback
Unlike conventional learning, where practice experiences might not be easily replicated, VR does not limit attempts. Trainees can practice procedures several times, and they will gain and build on experience with every trial. Further, most VR platforms offer performance feedback to the learners, ensuring they master when and where to apply different information, thus improving the learning process.
The Role of Virtual Reality in Modern Medical Education
VR Medical Training provides a rich learning environment that can supplement current resources such as mannequins, case-based approaches, and simulations.
How VR fits into the educational landscape
VR supplements traditional medical training and does not replace it, which is quite logical. For instance, a student can practice procedures involving a mannequin and concurrently see the anatomical structures in VR, thus enhancing learning. VR in Healthcare Education enhances case-based learning by enabling learners to explore simulated patients’ interactions and diagnose within the virtual environment.
To this end, VR provides learners with an environment similar to the real world in which they can practice what they have learned in class. Students can review the concepts of anatomy in depth, move virtual organs around, and perform operations, which will help strengthen their knowledge of the subject.
Immersive Learning Environment
Virtual Reality can provide procedures to students, as realistic, low-risk situations can help prepare learners for high-stakes events. From emergency response to intricate operations, Virtual Reality in Medical Training allows students to practice with realistic simulations as often as needed. Self-organizing VR places learners in an environment relevant to the learning context, entirely relying on their vision, hearing, and sometimes touch. Haptic feedback, incorporated, mimics the texture of medical instruments and body tissue to reinforce muscle memory.
Key Applications of Virtual Reality in Medical Training
Surgical Training
New trends in surgical training now include Virtual Reality, which allows for the training of procedures like orthopedics, neurosurgery, and cardiac surgeries. Through VR, one can even rehearse complex operations under conditions as real as can be painted in a virtual environment. Among the mentioned benefits is the repetition of procedures many times, which can be beneficial without placing patients at risk. The performance of VR Medical Training is that trainees can improve their techniques, enhance precision, and gain confidence while practicing in a risk-free environment, proving VR Medical Training is a vital resource for mastering surgery.
Emergency Medicine and Trauma Training
VR Medical Training also shifts the existing emergency medicine and trauma training models. In this case, doctors can get role-play experience when handling sensitive emergencies such as multiple casualty events, cardiopulmonary arrest, or traumatic injury. In VR, it is possible to predict patients’ reactions and perform interventions, which makes it possible to develop quick responses and decision-making. This preparation is essential, especially in actual situations, since this is where these types of decisions can make the difference between life and death.
Anatomy Learning
Among all the mentioned virtual reality applications, it’s in anatomy learning that virtual reality has been most effective in medical training. From the above-discussed finding, it can be understood that through VR, students can better understand the model of the human body in three dimensions to what they could get in texts or cadaver dissection. Through the site, learners can probe and experiment with organs, systems, and tissues and dissect and reconstruct actual anatomy. It also gives a deeper understanding and ensures that what the students learn is well retained, making VR in Healthcare Education an effective way of expanding knowledge of human anatomy.
Remote Learning & Collaboration
Besides the advantage of improving practical knowledge, Virtual Reality Medical Education promotes distance education and cooperation. The VR tools also facilitate teaching and collaboration, peer assessment, and even mentorship across geographical locations. Universities have found the use of VR technology in teaching medical students and even medical practitioners in virtual classes or simulations. This technology supports the live interface and practice of the case, which makes the constructs of medical education reachable and inclusive of the distance.
Benefits of Virtual Reality in Medical Training
Safe and Risk-Free Environment
Virtual Reality in Medical Training explains how students and professionals practicing medical procedures do not harm the lives of actual patients. This makes it possible for the learners to practice in surgery or trauma without exposing patients to their maneuvers. This peculiar advantage of VR makes it more applicable for simulations of training for health practitioners, whereby accuracy is considerably essential.
Repetition and Mastery
Another advantage of VR Medical Training is that it allows one to perform the exercises as many times as necessary, which is impossible in real-life training. Trainees can rehearse actions regardless of what they are—making a precise surgical operation or responding to an emergent situation. This repetition is significant because learners make mistakes in a virtual environment where they can suffer no penalties in the real world, making it easier for them to progress as the session continues.
Immediate Feedback
In particular, Medical Training with VR typically employs avatars of virtual tutors who can immediately analyze and evaluate the trainees’ actions. When trainees carry out procedures or deal with medically related incidents, the system records their performance, evaluation, and recommendation on the best strategy to take. It thus enables learners to get feedback on their work, modify it, and improve it in the shortest time possible, hence improving their skills and experience in their learning process.
Cost-Effective Training
Thus, the costs of learning with VR are considerably lower compared to traditional means that involve cadavers, physical simulators, and necessary tools. Once implemented, virtual Reality Medical Education tools can be used repeatedly, so they are cost-effective for institutions. This concept makes it possible for more students to train at higher standards compared to how it could have been if this was conducted using such many concrete physical assets.
Emotional and Psychological Preparation
In addition to technical competencies, the students are trained for the emotions and psychology of pressure surrounding high-stakes medical events. The use of VR means that learners can be put through the paces in a high-pressure situation, a traumatology case, or a critical surgical operation, for instance. This way, students get more prepared to face these scenarios in real life and know how to behave emotionally in case of real emergencies.
Challenges and Limitations of Virtual Reality in Medical Training
Cost and Accessibility
IT Consultancy Designed Around Your Business Objectives
Expert Guidance to Optimize Your Technology Strategy
Discover IT ConsultingAlthough Virtual Reality in Medical Training has recurring non-recoverable costs, the initial costs of owning high-quality VR hardware and software can be steep. High-end VR systems such as headsets, computers, and software are expensive, and relatively small organizations or developing nations can hardly afford most of them. Consequently, VR Medical Training may be restricted in some way due to accessibility issues; in other words, the advanced form of medical education may not be easily available for everyone.
Learning Curve and Technical Limitations
As with any new method of teaching and learning, there is the familiarization process, especially for educators and learners undertaking Medical Training with VR. Learning the technology requires some time, meaning there will be a slow pace of adoption at the beginning. Moreover, the current user experience in VR, which involves visualization, touch, hearing, and even smell, is not perfect due to the technologies, resolutions, or medical simulations. Still, as these technologies proceed to enhance, some of these technical constraints may affect the quality of training.
Overreliance on VR
While virtual reality medical education is very helpful, nothing can beat hands-on practice in the real world despite using first-person views. It is feared that reliance on this training technique may hinder the ability of students to gain exposure to real-life patients necessary in practical training. The work described of VR in Healthcare Education must be efficient and modest in the use of VR because while as a tool, it is powerful, it cannot truly replicate working with actual patients, especially in acknowledging the patterns of human behavior and manner of treating patients.
Current Technologies in Virtual Reality for Medical Training
Popular VR Platforms for Medical Education
Several emerging VR platforms are considered the future of virtual reality in medical training. Common-headed mounted systems such as Oculus Quest and HTC underpin the training simulation requirement owing to their vivid display and mobility in different medical training programs. Companies such as Osso VR and Touch Surgery offer surgical simulations, which allow trainees to learn intricate procedures in truly imitative, adjusted practice environments. These systems are built for medical practice with the intention of the doctors practicing on them to gain the muscle skills required to conduct surgery on actual patients.
Oculus
One of the most popular interfaces for VR in education, including medical ones, is the Oculus platform created by the Meta company, ex-Facebook. First, the Oculus Rift headset and the Oculus Quest have high-quality resolution visuals and quality controls, hence making them suitable for creating intensive medical training simulations. These headsets find application in different service delivery training, such as surgery processes and manners of interaction with patients, making it an all-in-one device for medical trainers.
Invest in Professional UX/UI Design to Create Impactful Interfaces
Designing Seamless User Journeys That Boost Interaction and Conversion Rates
Discover UI/UX DesignHTC Vive
HTC Vive is another popular VR platform that is noted for its accuracy and engaging experience. The latest among the Vive series, the Vive Pro series, is widely used in medical training due to features like the advanced tracking system and high-resolution display. It enables a close and vivid representation of the various intensive medical procedures to provide trainees with the best virtual learning experience. Using haptic feedback devices also gives the trainee the touch sensation to improve the training.
Osso VR
Osso VR is a virtual reality platform that trains people in specific surgery-related skills. Its comprehensive libraries of surgical operations allow the trainees to practice the operations and hone their skills within a risk-free modality. Through high-fidelity stereoscopic models with realistic haptic feedback and accurate reviews, Osso VR builds the competence and self-efficacy of medical personnel during operations.
Touch Surgery
Another category is Touch Surgery, a mobile-based virtual reality application with interactive surgical models. It is popularly used for competency-based training and to assess surgeons’ competency levels in different surgical disciplines. The platform has clear, scripted tutorials and feedback options, making it a helpful tool for surgeons’ initial, post-learning, and experience levels. Touch Surgery is also not limited by its access to fixed hardware and software and may be used in remote training.
Software Solutions
As with hardware, many rather popular software solutions focus on various aspects of medical education. Fundamentally, surgical procedures modeled by FundamentalVR entail very highly realistic displays of haptic sensations, including the texture of the tissues felt by the surgeon. In terms of services, Medical Realities provides courses containing a series of mental justice modules for anatomical learning and patient contact, together with surgical recommendations. It allows the students of medicine and health care professionals to practice what they learn in a realistic and virtual environment that helps them better understand body structures and get better at surgical operations.
AI and Machine Learning in VR Medical Training
Experience Our Research & Development Expertise
R&D-Led Software Development Integrates Innovation into Every Product Detail
Learn About R&D ServicesWith AI/Machine learning in VR in Healthcare Education, Training goes up a notch as learners will be accorded individual and interactive Contracts. AI-integrated virtual reality training can be more beneficial in learning, where the system can monitor the trainee and give real-time feedback or even provide recommendations on improving a particular skill. These platforms use machine learning to follow the learning progress of each learner and thus adjust the difficulty of the scenarios presented or create complicated, individualized patient cases. This, coupled with using AI in assessment, allows trainees to identify areas deficient in their performance. As a result, Virtual Reality Medical Education is an excellent tool for professional growth and improvement.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of VR in Medical Training
Harvard Medical School
Among various universities, Harvard Medical School has been one of the pioneers in using virtual reality (VR) as a tool for teaching medical courses. One such initiative worth highlighting is the application of VR education in explaining human anatomy. With the help of VR technology, students can get an accessible and detailed view of the human body in the virtual reality environment. It also enables one to study the relations of the different structures within the body, which is otherwise difficult by book study.
Also, at Harvard Medical School, VR is used in surgical procedure training and as a simulation. Generally, these simulations offer a safe ground for students to develop their skills without risking anything. For instance, last year, the faculty of the Department of Ophthalmology incorporated VR to enhance the approach to surgical education, especially in microsurgery. Through the VR simulations, the trainees simulate practices on delicate procedures in a way that receives feedback and performance evaluations in real time1. This approach increases competencies in technical aspects of surgery and instills confidence in aspiring surgeons.
Imperial College London
Applying Virtual Reality in Training of Trauma Surgery and Emergency Services
Imperial College London has been noted as the institution that first applied virtual reality to train medical students in trauma surgery and emergencies. The institution has stated that it has produced simulations based on virtual reality that expose students to the most critical aspects, such as cardiac arrest cases and major trauma cases. These training models are meant to present an ER’s ‘real life’ conditions, making the participants apply themselves quickly in their decision-making and response patterns.
One of these is branched scenarios—a peculiarity of Imperial College’s VR training. These scenarios offer the trainees multiple-choice questions and proceed depending on their decision. Students learn best when they can relate to the happenings of real life, and this technique affords them this opportunity. The college’s digital media lab designs all the VR training modules to fit the needs of medical processes.
New York City Teaching Hospital
One of the largest teaching hospitals in New York City has begun to incorporate Extended Reality (XR) into the training of anesthesiology residents. The population size in this center meant that conventional training methods hitherto were somewhat impractical, mainly because of the large number of residents. Through VR, the hospital provides flexibility, such as ACLS certification training, for which residents can train independently. It also benefits in getting through to the residents and meeting their soft skill needs like communication and empathy in addition to ensuring consistency of training.
University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB)
The University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB) has implemented VR technologies to simulate healthcare scenarios in its schools of Medicine, Nursing, and Respiratory Care as the pilot program. These kinds of simulations allow students to get some essential practice regarding patient safety evaluation and the interviewing of patients using AI avatars. Education is dynamically designed so students get practical experience, which might be hard to come by in settings like remote areas.
BC Women’s Hospital
BC Women’s Hospital has adopted a VR training program to teach its healthcare providers the proper use of protection gear. The VR training improved the performance of the simulated HCWs by 70% for the simulation group for one practice attempt compared to 20% for the control group for the same procedure. From this case, it is possible to conclude that VR can effectively improve procedural training, mainly when practitioners are located in geographically distant or low-resource areas.
HTC VIVE’s Global Impact
HTC VIVE has been involved in the revolution of healthcare education by training more than 2,500 doctors and students using VR. Their VR courses include robotic surgical training and managing Violence in Emergency rooms. All these courses can be taken online, meaning practicing physicians or other specialists in different regions can obtain the best training.
King Salman Center for Disability Research
The King Salman Center for Disability Research has studied the employment of Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality in medical training, particularly for people with disabilities. In their research, they show how these technologies can be adapted to the needs of disabled persons so that they can engage in realistic simulation of specific clinical scenarios. It also helps improve their knowledge about medical procedures, aiding remote diagnosis and mental health treatment.
Mayo Clinic
The Mayo Clinic has been using VR Medical Training in its residency training and continuous education for physicians to expand medical education. Indeed, one of the more significant examples is the necessity for VR in surgical training in residency programs. People can hone their skills in performing specific surgeries through simulation techniques; hence, they do not have to engage in the hazards that are likely to occur in actual surgeries.
Further, the Mayo Clinic uses VR to train all its professionals in continuing education. Physicians can engage in VR-based training programs that may include all the medical professions and operations. These modules give physicians detailed information on their performance, enabling them to improve and learn about the latest medical developments. Thus, incorporating VR into the ongoing education guarantees that Mayo Clinic’s medical staff practices modern medicine in practice and research.
The Future of Virtual Reality in Medical Education
The Evolving Role of VR
Further advancements in virtual reality in medical education will be even more vibrant with augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR). These technologies will complement each other, so the blend of reality will bring a more interactive and flexible training environment. For instance, AR could provide information on real-patient affairs, and MR could combine physical with virtual models, allowing the student to switch between the actual and the virtual environments. Integrating these technologies, such as VR, AR, and MR, will offer learners improved training experience and options for acquiring the desired skill and enhancing knowledge in clinical decision-making.
Making Product Discovery Easier and More Accessible
Turn Your Vision into a Reality in Four Weeks with Our Expert-Driven TechBoost Program
See Product Discovery ServicesAI Integration
As the technology of enhancement of artificial intelligence deepens, its incorporation in VR Medical Training will transform adaptive learning. In future versions of VR platforms, the strategies that apply will most likely incorporate AI to provide personalized learning pathways concerning the learner’s performance in the lessons, with variations in the level of difficulty of the scenarios that will be in operation in real-time. AI could also give formative evaluations to account for development over time to show the strengths and weaknesses of a trainee with a focus on the areas of improvement. This deeper integration of AI will also make VRME even more personal with better and perfect training techniques for every person.
Expanding Accessibility
Although cost is a challenge to many institutions today, it is hoped that the costs of VR in Healthcare Education systems will come down in the future. According to technological advancements, hardware prices are expected to keep falling, allowing more medical facilities and schools in developing nations to afford VR. There will also be improved accessibility concerning cloud-based platforms and portable VR devices, enabling students to undergo advanced medical training without investing in costly equipment. The above expansion in accessibility will eventually lead to the availability of quality medical education for the citizens in every country.
Ethical Considerations
With IMTA of the VR Medical Training taught in the health care learning curve as a reality, isolated and emerging issues about the ethic and human touch impact assessment will emerge. Compared to the technical aspects of medical practice, VR can only replicate the actual practice to a certain extent without addressing the patient’s emotions and personal relationship with them. One of the strategies that need to be employed with more vigor to avoid the elimination of ‘hands-on’ physical contact with patients is to ensure that the VR applications do not entirely replace real patient interactions. In that sense, medical educators will need to walk a fine line between presenting ability development through technology and keeping the human touch of the medical profession necessary for patient care and the success of the healthcare field.
Embracing the Future: The Transformative Power of Virtual Reality in Medical Training
Virtual Reality Medical Education is transforming the way healthcare professionals are trained. By providing cost-efficient, immersive, and risk-free environments, VR addresses many of the limitations of traditional medical training. As the use of VR in Healthcare Education continues to grow, it is becoming an indispensable tool for ensuring that medical professionals are well-prepared for the complexities of patient care. Investing in VR Medical Training is an investment in the future of healthcare, offering students and professionals a new way to learn, practice, and perfect their skills.
Schedule a meeting, and let’s discuss how our team of experts can help you stay ahead of the competition!
What is virtual reality medical training, and how does it work?
Virtual reality medical training is a practice that uses immersive, computer-generated environments to simulate real-life clinical situations. With VR software and headsets, medical students and practitioners can engage with 3D anatomical models, practice procedures, and participate in patient simulations. This is a technology that simulates a real-life scenario in a safe, controlled environment, which facilitates learning by visualizing, repeating, and participating.
Does VR improve learning outcomes in medical education?
Yes, several studies have demonstrated that virtual reality significantly affects knowledge retention, skill acquisition, and confidence. Intensive practice and application, which could be obtained through VR rather than traditional methods, led to enhanced performance in the real-world clinical setting.
How is VR used for surgical training in healthcare?
Surgical training is one of the broadest applications of VR, which simulates complex operations, such as orthopedic, cardiac, and neurosurgery. The trainees are in a risk-free environment where they can realistically simulate a life-like operation using real instruments. Training tools such as Osso VR and Touch Surgery are also step-based and provide performance feedback, allowing learners to develop precision and muscle memory.
Can VR replace cadavers and improve anatomy learning in medical school?
VR enhances anatomy education through 3D, interactive visualization of the human body. Learners are able to do virtual dissections, rotate organs, and examine systems from different angles. Although it does not entirely affect the practice of cadaver labs, VR greatly complements the traditional way of learning anatomy, particularly in cases where cadavers cannot be used.
What types of medical procedures can be simulated with VR?
VR can mimic virtually any procedure, including surgical operations, emergency interventions, patient evaluation, and diagnostic work. VR enables learners to train across specialties with high levels of realism and repeatability in trauma care and general clinical practice.
Is virtual reality effective for emergency and trauma training?
VR is indeed effective in training emergency medicine. It emulates the conditions of high stress, such as cardiac arrest or mass casualties, and the students can work on decision-making, collaboration, and critical thinking skills in time-sensitive settings without exposing the patients to risks.
What are the main benefits of using VR in medical education?
One of the main advantages of VR in healthcare education is immersive, hands-on, risk-free, and safe learning; cost savings; expanded access; real-time feedback; and increased learner confidence. It enables practice and exposure to rare or complex cases, thereby increasing technical and soft skills.
Is VR medical training more cost-effective than traditional methods?
In the long run, VR training will be more affordable compared to traditional training. It eliminates the use of cadavers, physical simulators, and big teaching rooms. Once implemented, VR systems can be used by many learners, reducing long-term operational and material costs.
What are the challenges of using VR in medical training?
Issues such as the initial cost of equipment and software, student and teacher education and training, potential motion sickness among some users, and existing shortcomings in haptic feedback have been noted. Also, VR should be combined with actual patient interaction to build bedside manner and clinical intuition.
How realistic is VR medical training? Does it include haptic feedback?
VR medical simulation in modern realities is highly realistic, with elaborate visual and auditory cues. Other systems, such as FundamentalVR, incorporate haptic feedback to form the tactile sensation of tissues and instruments. Nevertheless, complete physical realism is yet to be developed and differs across platforms.
Which VR platforms and tools are best for medical training?
Top VR platforms include:
- Osso VR – for surgical training.
- Touch Surgery – for interactive simulations.
- FundamentalVR – for haptic-enhanced surgical simulations.
- HTC Vive and Oculus Quest – hardware used widely in VR education.
These tools offer customizable training programs for medical schools, hospitals, and individual learners.
Can VR be used for remote or online medical education?
Yes, remote learning is possible with VR, enabling students and instructors to interact in virtual space regardless of their locations. It helps support peer collaboration, online classrooms, and self-paced simulations, bringing high-quality medical education closer and more accessible.
Does VR in healthcare education provide students with real-time feedback?
Absolutely. Most VR training programs use AI-based feedback systems to assess performance, inform decision-making, and identify areas for improvement. This real-time feedback enhances the learning process and enables the individual to improve their skills more quickly than with delayed assessment methods.
How accessible is VR medical training for small institutions or developing countries?
Although the first solution might be expensive, VR’s scalability over time makes it more affordable. With declining hardware costs and growing cloud-based system sizes, even small institutions can begin using VR to deliver consistent, high-quality training without investing in extensive physical systems.
Will virtual reality replace real patient care in medical training?
No. VR is an effective supplement, not a substitute for face-to-face patient care. It trains learners in clinical settings by developing their skills and confidence. Nevertheless, practical experience is necessary to learn how to deal with people, provide bedside care, and make on-the-job decisions.