In the dynamic world of financial technology, understanding the latest trends is more than just a competitive advantage—it’s crucial for sustained relevance. The fintech space has expanded exponentially. As of 2023, it’s valued at a staggering $179 billion, with approximately 30,000 fintech startups scattered globally. The Americas lead with 11,651 startups, followed closely by EMEA at 9,681 and the Asia Pacific housing 5,061. It’s interesting to note the leading fintech unicorns in the United States as of April 2023: Stripe, valued at $95 billion; Coinbase, with a valuation of $68 billion; and Robinhood standing strong at $40 billion.
While the global fintech investment dipped to $164.1 billion across 6,006 deals in 2022 from a record high of $238.9 billion across 7,321 deals in 2021, it’s evident the industry remains vibrant. A deep dive into the sectors reveals that payments took the lion’s share in 2022, attracting $53.1 billion in investments, with RegTech following at $10.6 billion.
As the CTO of HyperSense Software Inc., a company with a two-decade legacy in specialized FinTech development, I’ve been at the forefront of this evolution.
Custom Software Perfectly Aligned with Your Strategic Objectives
Software Solutions that Fit and Enhance Your Business Strategy
Explore Custom SoftwareThe Rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance, commonly known as DeFi, is revolutionizing the financial landscape. Thanks to blockchain technology, it’s a shift from traditional, centralized financial systems to an era where protocols and platforms run without intermediaries.

DeFi By the Numbers
- As of January 18, 2023, the DeFi market stood at a notable $45.33 billion and projections show an ascent to over $231 billion by 2030.
- The total value locked (TVL) in global DeFi platforms across diverse blockchains reached an impressive $154.5 billion by November 2022.
- Leading the pack in TVL as of January 18, 2023, were DeFi platforms Maker with $9.8 billion, Aave with $8.9 billion, and Compound at $7.4 billion.
Real-life Applications of DeFi
- Banking: Move over traditional banks; DeFi offers services ranging from savings and loans to investments and payments without bureaucratic red tape.
- Remittances: No more intermediaries, high fees, or delays; DeFi ensures swift, economical, and secure cross-border transfers.
- Insurance: A world where insurance is transparent and trustless, as users pool resources and collectively share risks.
- Supply Chain Management: Enhance efficiency and traceability in supply chains with smart contracts automating, verifying, and enforcing agreements. Blockchain ensures a foolproof record of the product’s journey.
- Identity Verification: Users now wield control over their identity and data. A self-sovereign identity is network-verified and universally usable across different platforms, with data-sharing at the user’s discretion.
- Social Impact: Beyond profitability, DeFi also promises a positive societal change, granting financial inclusivity for the unbanked and supporting noble causes like disaster relief, education, and healthcare.
- Real Estate: DeFi is set to disrupt real estate, trimming costs, boosting liquidity, and ensuring transparency. The tokenization of real estate assets, loans, mortgages, and decentralized rent payments are just the tip of the iceberg.
Though DeFi’s trajectory looks promising, challenges persist, from smart contract vulnerabilities to regulatory uncertainties. Yet, as technological solutions evolve, the potential of DeFi to redefine not just fintech but the broader financial realm remains unparalleled.
Experience Our Research & Development Expertise
R&D-Led Software Development Integrates Innovation into Every Product Detail
Learn About R&D ServicesAI-driven Financial Analysis
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is swiftly becoming the backbone of modern financial systems. With its ability to process vast amounts of data in real-time and make sense of intricate patterns, AI’s role in the financial world has moved from a futuristic vision to a present-day reality.
Market Overview and Adoption
- With projections pointing to a $407 billion valuation for the AI market by 2027, finance is emerging as a dominant player in AI adoption and investment.
- The finance sector has seen an exponential adoption rate of AI since 2017. However, a curious trend has been observed, where the percentage of organizations embracing AI has stabilized, hovering between 50 and 60 percent in recent years.
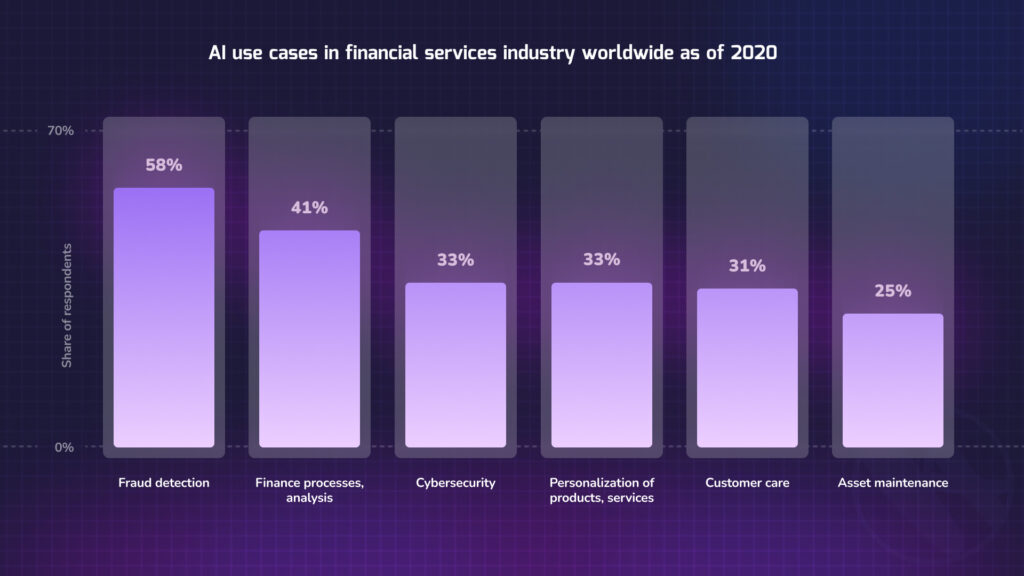
Real-world Applications of AI in Financial Analysis
- Credit Decisions: Gone are the days of manual loan approvals. AI now assesses creditworthiness, automates loan sanctioning, and personalizes interest rates and repayment plans.
- Quantitative Trading: The stock market is no match for AI’s prowess. Traders leverage it to decipher market patterns, pinpoint trading avenues, execute timely trades, and refine portfolios.
- Financial Risk Management: The financial world is rife with risks. AI monitors and mitigates threats, be it credit risk, market fluctuations, operational hiccups, or liquidity challenges.
- Fraud Detection: Security is paramount, and AI is the watchdog. It sniffs out fraudulent transactions, identifies theft attempts, combats money laundering, and thwarts cyberattacks, thanks to its mastery in anomaly detection, pattern discernment, and natural language processing.
- Customer Service: The age of waiting is over. AI-driven chatbots, voice assistants, robo-advisors, and tailor-made suggestions elevate customer interactions to new heights.
- Portfolio Management: Financial experts and casual investors alike are reaping the benefits of AI. Real-time monitoring, intricate risk assessments, and intuitive rebalancing advice revolutionize portfolio management.
- Regulatory Compliance: AI is the compass in a maze of ever-evolving regulations. It’s automating tedious tasks like data collation, reporting, auditing, and verifications, ensuring financial bodies remain compliant without breaking a sweat.
AI’s integration into finance enhances efficiency and reshapes the industry’s foundation. As the AI wave continues to rise, its potential to redefine financial analysis and operations is promising and exciting.
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) is reshaping how we perceive and interact with banking services in the ever-evolving financial ecosystem. BaaS fosters a symbiotic relationship between traditional banks, fintech companies, and non-financial entities by democratizing access to banking capabilities and operations.
Growth and Potential of Banking-as-a-Service
- Beginning with a valuation of $2.41 billion in 2020, the global BaaS landscape has shown a robust projection, expected to burgeon to $11.34 billion by 2030, charting a CAGR of 17.1% from 2021.
- Notably, the US has emerged as a BaaS powerhouse. With a whopping $637.40 billion valuation in 2022, the trajectory is poised to skyrocket, anticipating a reach of $6,943.49 billion by 2030, with a stunning CAGR of 32.9% from 2024.
- An attractive proposition for banks and fintechs alike, BaaS promises up to 95% cost savings on customer acquisition, dwarfing traditional methodologies.
- Beyond standard services, BaaS paves the way for embedded finance, integrating financial capabilities into unconventional platforms. From a substantial $22.5 billion in 2020, embedded finance is poised to generate a revenue of $230 billion by 2025.
Real-world Applications of BaaS
- Real-time Payments: No more waiting games. BaaS platforms champion real-time mobile buys, QR code transactions, merchant-driven activities, and peer-to-peer transfers, leveraging simple identifiers like e-mails or phone numbers.
- Embedded Banking: BaaS opens doors for entities beyond banks. Think e-commerce giants, your favorite ride-hailing services, or even the social media platforms you frequent – all potentially offering banking amenities, from loans to cards.
- Open Banking: Fragmented financial data is passé. BaaS ensures a seamless panorama, allowing users to access and manage their financial narrative across providers, underpinned by APIs and fortified authentication.
- Neobanking: Digital-only banks are no longer a part of sci-fi. Thanks to BaaS, fintech pioneers craft digital banks that cater to the contemporary user with budgeting, savings, and investment tools.
BaaS is not just a trend but a paradigm shift, redefining the boundaries of banking and promoting inclusivity and innovation. As we journey through this decade, the amalgamation of technology and finance via BaaS is poised to usher in a new era of digital empowerment.
Making Product Discovery Clear and Accessible
Transform Concepts into Products in Four Weeks with Our Proven TechBoost Program
See Product Discovery ServicesContactless & Biometric Payments
Payment methods are present in an age swiftly gravitating towards instantaneousness and hygiene. Contactless and biometric payments, marked by technological finesse, transform our financial transaction experiences.
Contactless payments deploy RFID or NFC technologies to ensure a transaction happens without the card physically touching the Point-of-Sale terminal. Biometric payments use one-of-a-kind human identifiers such as fingerprints, facial patterns, or voice signatures to authorize transactions.
Contactless & Biometric Payments By the Numbers
- A significant leap was seen in 2021 when over two-thirds of retailers adopted some form of contactless payment. Specifically, contactless cards jumped from 40% in 2019 to 58% in 2021, and mobile digital wallet payments grew from 44% in 2019 to 56%;
- The global arena of contactless biometric technologies stood at $6.92 billion in 2019. With a staggering expected CAGR of 19.1% from 2020 to 2027, it’s set to burgeon to $28.83 billion by 2027;
- Facial recognition is emerging as the dominator of these technologies, holding 32.6% of the global market in 2019.
Transforming Real-world Interactions of Contactless & Biometric Payments
- Contactless Kiosk & Mobile POS Payments: With innovations like those from Payface in Brazil, customers can use facial biometrics combined with liveness detection, offering a transaction devoid of the need for tangible cash, cards, or phones.
- Biometric Sensor Cards: Organizations like Thales equip banks with cards that use fingerprint biometrics, providing a swift and secure payment both in contact and contactless scenarios. All this without the need for POS terminal software modifications.
- Reimagining ATM Interactions: Diebold Nixdorf is paving the way for banks to offer their customers cardless and PIN-less ATM transactions. Accessing bank accounts and withdrawing money is revolutionized using face or iris biometrics.
In essence, the surging prominence of contactless and biometric payments signals technological advancement and resonates with the evolving demands and preferences of the global population, pivoting towards safety, convenience, and speed.
Financial Literacy Tools
The shifting sands of the global financial landscape underscore the urgent need for enhanced financial literacy. With innovative fintech solutions, the availability and accessibility of financial literacy tools have substantially increased.
A Global Perspective on Financial Literacy
The OECD/INFE 2020 International Survey, covering over 90,000 adults across 26 nations, highlighted a pressing concern: the average financial literacy score was a mere 13.2 out of 21. This indicates only a moderate level of global financial comprehension. However, the silver lining is that 59% of the global adult population has actively sought financial education tools in the last two years. Websites took the lead, with 35% utilization, trailed by books at 18%, apps at 17%, and courses at 16%.
The Role of Institutions in Promoting Financial Education:
The 2021 Financial Literacy Annual Report by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) underscores institutions’ monumental role in bolstering financial literacy. In just 2020, the CFPB’s far-reaching initiatives managed to engage with over 27 million consumers through diverse channels, including online tools, social media, and publications.
What Are Financial Literacy Tools?
These digital solutions range from apps to online platforms designed to instruct users on astute financial management, risk comprehension, investment insights, and long-term financial planning.
Tangible Implementations and Impact:
- Digital Budgeting: With budgeting tools, users can set financial boundaries, keep a vigilant eye on expenditures, and even project future spending patterns.
- Simulation-driven Investment: For those dipping their toes into investments, simulators provide a zero-risk environment to practice and hone their strategies.
- Planning for the Golden Years: Retirement planners demystify the financial challenges of the future, assisting users in preparing for their retirement phase.
- Navigating Debt with Clarity: Debt calculators elucidate debt scenarios, making repayment strategies more coherent and actionable.
- Engaging Education Platforms: Interactive modules, courses, and quizzes give users a comprehensive understanding of diverse financial subjects.
With the expansion of the digital financial ecosystem, it’s evident that integrating educational components becomes even more indispensable. These tools bridge the knowledge chasm, ensuring every user is adeptly prepared to manage their finances.
Personalized Banking Experiences
In the age of digital transformations, personalized banking experiences are emerging as a defining factor in securing and retaining customers. Personalization stands at the forefront as financial institutions explore innovative ways to engage with their clientele. However, this is not just a trend; statistics point towards a strong preference among customers for a tailored banking journey.
The Crucial Link Between Personalization and Loyalty
A compelling study revealed that a staggering 86% of individuals who value personalization expressed a higher likelihood of sticking with their current financial institution if it heightened its focus on delivering more personalized services. This highlights the power of customization in forging lasting bonds between banks and their customers.
Customers’ Willingness to Switch for Better Personalization
The World Retail Banking Report 2022, a collaborative study by Capgemini and Efma, brought some eye-opening insights to light. A significant 64% of customers indicated they wouldn’t hesitate to switch their bank allegiance if enticed by superior personalization from another service provider. Even more intriguing is the finding that 75% of customers were open to sharing additional personal data with their banks. In return, they sought enhanced personalized offers and services. This underlines the value of trust in the banking relationship, emphasizing the trade-off between data privacy and personalized benefits.
Measurable Benefits of Personalized Banking
The tangible impact of personalization on banking’s key performance indicators cannot be overstated. A study spearheaded by Personetics illuminated that 87% of leaders steering the customer experience in banking confirmed the positive ramifications of personalization. This encompassed vital areas such as customer satisfaction, loyalty retention, and even a direct surge in revenue.
Crafting Tailored Banking Experiences
Personalized banking is not merely about offering products that align with individual financial needs. It’s about predictive analytics that can anticipate a customer’s next move, seamless integration of banking channels for a uniform experience, and fostering a relationship built on trust and understanding.
Green and Sustainable Finance
With growing environmental concerns and societal shifts, the financial sector has promptly embraced green and sustainable finance. This approach integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into investment and banking decisions, aligning with global sustainability goals, such as the Paris Climate Agreement.
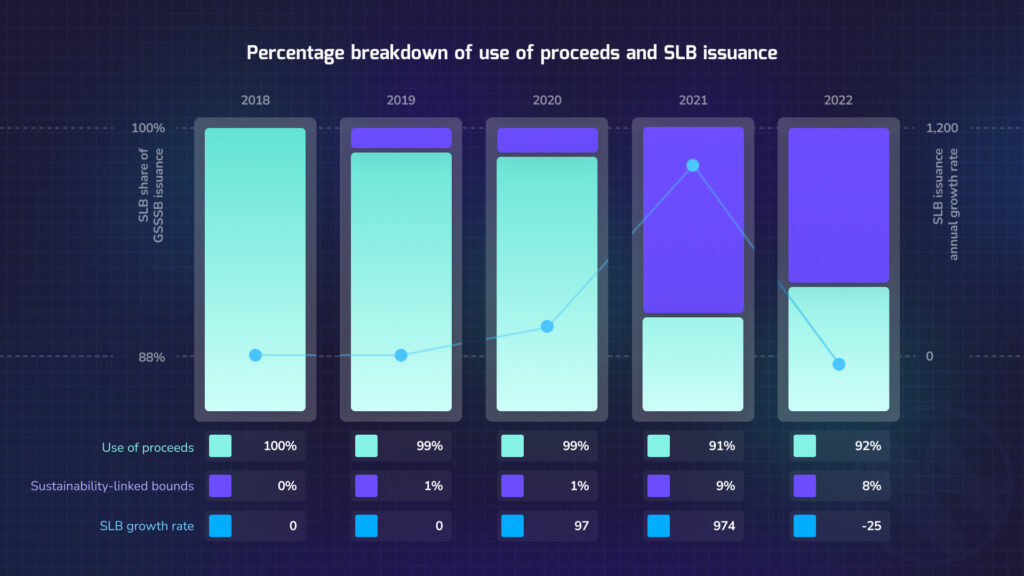
Sustainable Finance and Social Responsibility
While green finance primarily targets environmental issues, sustainable finance takes a broader approach. It incorporates both environmental and social considerations, ensuring that financial practices contribute to societal well-being. This could involve supporting projects that aim for clean water, affordable housing, or even quality education – all essential elements for a just and prosperous society.
Quick Facts:
- The Bank for International Settlements notes that green bond issuances globally reached $269 billion in 2021, an increase from $258 billion in 2020;
- As per the European Central Bank, sustainable debt securities saw their share grow from 1.5% of the total outstanding debt securities of euro area residents in 2019 to 2.4% in 2021.
Real-world Impacts of Green and Sustainable Finance
- Green Mortgages: Banks are offering favorable terms for loans on energy-efficient homes.
- Sustainable Platforms: Platforms such as “Betterment” enable ESG-aligned investments.
- Carbon Credit Trading: These platforms encourage reducing greenhouse gas emissions by trading emission allowances.
Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain, often linked predominantly to cryptocurrencies, boasts a myriad of applications that stretch far beyond just digital coins. Its decentralized and tamper-proof ledger has been instrumental in reshaping numerous industries, enhancing transparency, efficiency, and security.
- Supply Chain Verification: Companies like IBM have launched platforms such as the IBM Food Trust. These platforms use blockchain to trace products from their origin to the retail shelf, ensuring authenticity and reducing instances of fraud.
- Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts contain the terms directly written into code. They ensure that all stipulated conditions are met before any transaction is completed. Ethereum, for instance, is a popular platform for crafting such contracts.
- Digital Identity Verification: Blockchain provides a secure framework for digital identities, granting users control over their data. Microsoft’s ION is a notable decentralized identity system using this technology.
- Intellectual Property & Royalty Tracking: Artists and creators can track the use of their work and ensure proper royalties are received through blockchain-based systems.
- Voting Systems: Countries like Estonia are exploring blockchain for its potential to host secure, transparent, and tamper-proof voting systems.
- Healthcare and Medical Records: Blockchain allows for the secure sharing and storage of medical records among approved professionals, ensuring privacy and accessibility.
The Surge in Regulatory Technology (RegTech)
Regulatory Technology, or RegTech, emerged as an antidote to the complex regulatory environment that financial institutions navigate. It utilizes advanced technologies to automate and streamline compliance processes, allowing for more efficient and cost-effective adherence to rules and regulations.
Regulatory Technology by Numbers
The global RegTech landscape has been experiencing exponential growth. As of 2019, the market size stood at USD 2.18 billion and is forecasted to swell to USD 10.36 billion by 2026, registering an impressive CAGR of 24.7% from 2021-2026. This rapid expansion is a testament to the growing need for advanced solutions in the face of mounting regulatory challenges.
A benchmarking report by the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance illustrates the global distribution of these firms. In 2019, there were over 400 RegTech firms worldwide. North America led the market, accounting for 38% of the sector, with Europe tailing closely at 29%. The Asia-Pacific region was just a little behind, holding a 22% market share.
Emerging Applications of RegTech
RegTech applications are as diverse as they are promising. As per a speech by the International Monetary Fund, some of the groundbreaking applications include:
- efficiently mapping and regularly updating regulatory obligations;
- streamlining processes to reduce costs and bolster regulatory compliance significantly;
- conduct risk management, which includes monitoring financial institutions’ sales calls to ensure adherence to best practices.
IT Consultancy Designed Around Your Business Objectives
Expert Guidance to Optimize Your Technology Strategy
Discover IT ConsultingBenefits of RegTech
According to a white paper released by the World Economic Forum, the benefits of RegTech are manifold:
- Cost Efficiency: One of the primary advantages is reducing regulatory burdens and associated costs;
- Enhanced Data Management: Improved data quality and availability not only aids in compliance but also bolsters decision-making processes;
- Risk Management: With advanced tools, financial institutions can better identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks;
- Innovation and Collaboration: RegTech platforms foster an environment conducive to innovation, ensuring that financial entities remain ahead of the curve while also promoting collaboration.
FinTech for Financial Inclusion
The integration of technology into finance, commonly referred to as FinTech, holds transformative power. One of its most promising avenues is the potential to bridge the financial inclusion gap, providing underserved populations access to critical financial services.
Why Financial Inclusion Matters?
Financial inclusion means ensuring that all individuals have access to useful and affordable financial products and services regardless of their socio-economic status. This includes basic banking, credit, insurance, and other financial resources.
FinTech plays an instrumental role in driving this agenda forward by:
- Facilitating Digital Payments: Mobile wallets and online payment platforms enable users to transact without traditional bank accounts. Such platforms often require just a basic smartphone, making them accessible to many.
- Microfinancing: FinTech firms can leverage data analytics to assess creditworthiness differently, offering micro-loans to those traditionally deemed “high risk” by conventional banks.
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) Lending: P2P platforms bypass traditional financial intermediaries by directly connecting borrowers to lenders, often leading to more lenient loan terms and conditions.
- Financial Literacy and Education: Several FinTech apps and platforms offer educational content, equipping users with knowledge about savings, investing, and managing finances.
Benefits Financial Inclusion
- Economic Growth: When more people can access and use financial products, there’s an increase in investment, job creation, and overall economic growth.
- Poverty Reduction: Access to credit can provide life-changing opportunities, from starting a small business to funding education.
- Empowerment: Financial inclusion, especially among women and marginalized communities, can foster a sense of independence and empowerment.
Cutting-Edge Mobile App Development for Success
Mobile Solutions that Connect Your Business with Your Market
Explore Mobile App DevelopmentConclusion: Envisioning the Dynamic Future of FinTech
As we navigate through the myriad facets of FinTech, one underlying theme emerges: the financial sector is in a perpetual state of evolution, driven by the relentless march of technology. This dynamic interplay between finance and technology underscores the present and illuminates the path to a promising future.
The very essence of FinTech lies in its capacity for innovation, breaking boundaries, and reshaping conventional financial paradigms. Each advancement, from blockchain to RegTech and personalized banking to green finance, is a testament to how technology continuously breathes new life into the finance realm.
Moreover, the fusion of technology with finance has begun to redefine opportunities, leveling the playing field for many and expanding horizons for businesses and consumers alike. Whether it’s about reaching the unbanked corners of the globe, devising sustainable financial solutions, or tailoring personalized banking experiences, the possibilities seem limitless and exciting.
Yet, with these myriad opportunities, challenges invariably arise. As we progress, we must ensure that innovations are inclusive, ethical, and sustainable. Regulation, while often seen as a deterrent to innovation, will be pivotal in striking a balance, ensuring that the FinTech wave creates ripples of positive impact without causing tsunamis of unforeseen repercussions.
In closing, the world of FinTech stands at a fascinating juncture. It’s a nexus where tradition meets innovation, where risks meet rewards, and where challenges meet solutions. As we move forward, it’s clear that the story of FinTech is one of continuous transformation, and we’re just turning the pages of its early chapters. The future beckons with promise, potential, and unprecedented possibilities. It’s a journey worth watching—and participating in.