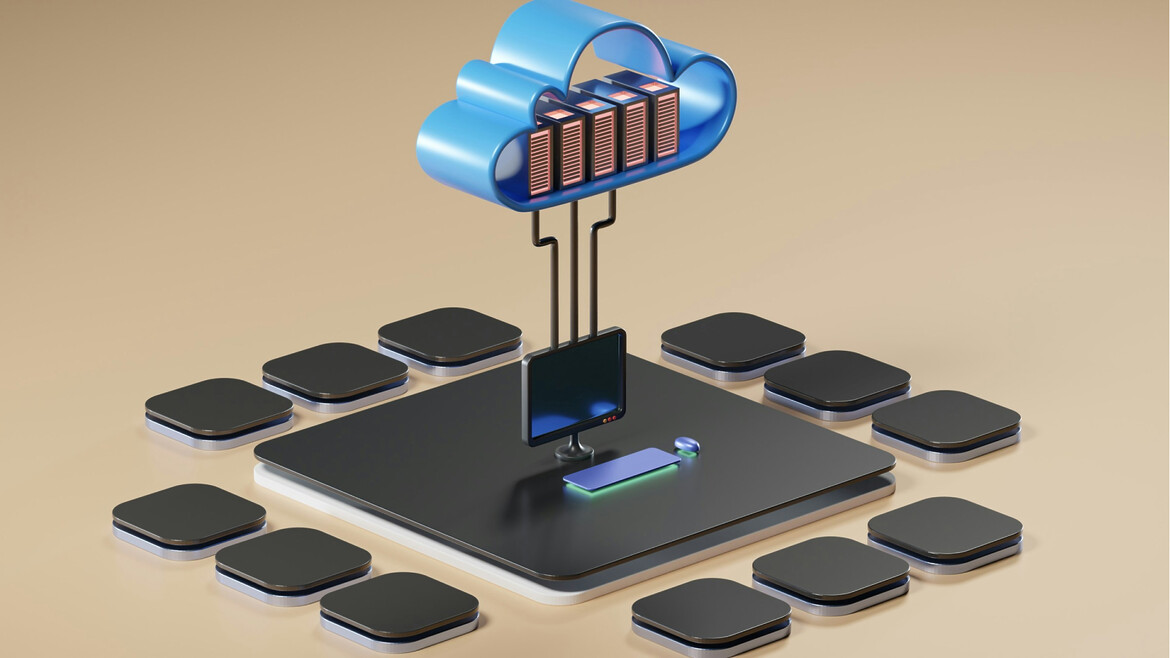
Edge Computing and Cloud Computing in today’s dynamic digital environment are transforming the computing environment for business organizations striving to maximize efficiency, minimize costs, and enhance customer value. In today’s competitive digital era, selecting the appropriate computing environment is a key strategic factor. Two widely adopted solutions—Edge Computing and Cloud Computing—each offer diverse benefits. But which one works best for your business? Both solutions boost the computational performance of devices and applications yet differ in their structures, deployment types, and applications. Understanding these differences is essential for companies aiming for higher results, lower costs, and a sustained competitive advantage.
If you’re looking to leverage these cutting-edge technologies, consider how our specialized Mobile App Development Services can drive innovation in your mobile strategy, while our tailored Web Development Services ensure your online presence is robust and future-ready.
Customized Mobile Apps to Elevate Your Business
Building Mobile Apps that Bridge Your Business with Your Audience
Explore Mobile App DevelopmentThis article will help you understand the peculiarities of both technologies, their differences, and how to make the right choice.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge Computing processes data closer to where it’s being generated, whether that’s a sensor, device, or local server. Instead of pushing raw data to centralized cloud servers, edge devices or local servers perform critical tasks to reduce latency and enhance real-time performance.
This federated approach is especially suited for applications needing fast response times, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial IoT, and remote healthcare. According to MarketsandMarkets, the proliferation of smart devices and connected systems is estimated to drive the global edge computing market, which is forecasted to grow from $36.5 billion in 2023 to $87.3 billion by 2027.
Key Aspects of Edge Computing

Low Latency
Latency reduction is one of the biggest advantages of edge computing. Edge computing involves processing data at the edge, near its source, which minimizes the time spent transmitting data from the device to the server. This is crucial for applications requiring real-time responsiveness, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, or augmented reality. In autonomous vehicles, even a small delay in processing data can lead to serious safety issues. Data processed nearly instantaneously enables real-time decision-making and enhances the performance of latency-sensitive applications.
Decentralized Processing
Edge computing decentralizes data processing by conducting computations on local devices, IoT sensors, or nearby servers. This approach eliminates reliance on centralized data centers and significantly reduces the data volume sent across networks. For instance, decentralized processing is particularly beneficial for IoT applications, where numerous devices generate massive amounts of data concurrently. In edge computing, data is processed locally, alleviating the burden on central servers and ensuring the operation of critical functions in the event of a loss of connection to the central server. This enhances system reliability and resilience.
Bandwidth Conservation
Local processing in edge computing eliminates the need to transmit large volumes of data to central servers, thus saving bandwidth and reducing costs. In traditional cloud computing models, considerable amounts of data are sent to centralized data centers for processing, leading to network strain and substantial data transfer costs. Edge computing addresses this issue by processing data at the network edge, where it is generated. This not only conserves bandwidth but also minimizes latency caused by data transmission. This translates into cost savings and efficient use of network resources for businesses.
Enhanced Privacy
Processing data locally in edge computing decreases the volume of sensitive information sent to remote locations, thereby enhancing data privacy and security. Protecting sensitive data is critical in the healthcare, finance, and retail sectors. Edge computing ensures that data is processed and stored as close to its source as possible, reducing the risk of data breaches during transmission. For example, in healthcare, patient data can be processed at the point of collection on medical devices or edge servers within a hospital, allowing sensitive information to remain encrypted and compliant with data protection regulations. The local data processing approach is beneficial for privacy and building customer and stakeholder trust.
Components of Edge Computing
Edge Devices
One of the biggest reasons to understand what edge computing is lies in the hardware involved: edge devices. Smartphones, sensors, industrial robots, and autonomous vehicles are a few examples of these devices. Edge devices process data at the source, reducing the need to transmit information to centralized servers, which decreases latency and enhances real-time responsiveness. For instance, in industrial automation, sensors on machinery can detect anomalies and take action immediately without waiting for commands from a remote server. Autonomous vehicles also utilize edge devices to quickly process substantial amounts of data from cameras and sensors to operate safely and effectively.
Network Edge
The critical point is known as the network edge, where data enters or leaves the network. It is responsible for forwarding data safely and quickly between edge devices and other parts of the network. Components such as routers, switches, and gateways, which control data traffic and secure data transfers, are part of the network edge. Handling data at the network edge enables businesses to alleviate the load on central servers and generally improve network performance. For example, in a smart city, the data collected from multiple IoT sensors, such as environmental changes, traffic conditions, and public safety incidents, is forwarded to local processing units at the network edge for quick processing responses.
On-Premise Infrastructure
Their hardware and software that supports edge devices (servers, routers, gateways, etc.) is also deployed on-premises. This infrastructure is essential for powering edge computing solutions and ensuring that data is processed and communicated seamlessly. On-premises servers provide computational power for data analysis and decision-making at the edge. Routers and gateways facilitate data transfer to and from edge devices and a larger network. For example, in a healthcare setting, patient data from various medical devices can be processed by on-premises servers in real-time to obtain diagnoses and treatments immediately, while maintaining data privacy and security maintained.
Edge Notes
Small, low-power devices known as edge nodes perform various functions, including data processing, content caching, and load balancing. Strategically located near the data source, these nodes execute specific tasks that minimize the distance the data needs to travel. Edge nodes can process data locally, cache frequently accessed content, and distribute workloads to enhance performance. For instance, in content delivery networks (CDNs), edge nodes store popular content closer to users, thereby reducing latency and improving the user experience. In IoT applications, edge nodes can aggregate and preprocess data from multiple sensors and transmit only relevant information to central servers for further analysis.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing is a solution model for delivering applications, storage, processing power, networking capabilities, and other IT services through the Internet. It is also known as the cloud. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provide available, easily scalable facilities that are charged only by usage. Gartner estimates that global spending on public cloud services will reach $597.3 billion by the end of 2024, up from $490.3 billion in 2022. This growth underscores the increasing demand for cloud solutions, which are key to business strategy, recovery, competitive advantage, and creativity.
Key Features of Cloud Computing
Scalability
Scalability is one of the most outstanding features of cloud computing. Businesses with fluctuating workloads will find that cloud services can easily scale up or down to meet demand, providing unparalleled flexibility. In other words, e-commerce platforms can quickly adjust their resources during peak seasons or promotional events. On the other hand, they can reduce their capacity during off-peak periods to cut costs. The dynamic scalability allows businesses to incur costs only for the resources they actually use, maintaining a balance between performance and expense efficiency.
Cost-Efficiency
One of the primary ways cloud computing reduces costs is by eliminating the expense of on-premises infrastructure. Traditional IT setups require a significant investment in hardware, software, and maintenance. In contrast, cloud computing operates on a pay-as-you-go model where businesses are charged for the resources they use. This model reduces capital expenditures and lowers operational costs, as cloud providers handle maintenance, updates, security, and other issues. This cost efficiency can greatly benefit startups and small businesses seeking the advantages afforded by state-of-the-art technologies without the financial burdens of traditional IT infrastructure.
IT Consultancy for Strategic Advantage
Tailored IT Solutions to Drive Your Business Forward
Discover IT ConsultingAccessibility
Cloud computing makes data and applications available from anywhere internet access is available. Today, with remote work becoming more common, this feature works great, allowing employees to work together anywhere and access resources from anywhere. Shared documents, real-time communication, and access to critical information from any device make it possible for team members to work together, regardless of geographic location or device. The accessibility provided at this scale improves productivity and creates a more flexible and agile workforce.
Centralized Management
Additionally, cloud computing is a key aspect of centralized management that facilitates the maintenance and updates of IT resources. In a traditional IT environment, managing and updating hardware and software across multiple locations can be cumbersome and time-consuming. These tasks are handled through cloud computing; centralizing them allows control of resources from a single control panel. By adopting a centralized approach, operations become simpler, the risk of errors decreases, and all systems remain current with the latest security patches and programming updates. Furthermore, cloud providers enable the administration of IT resources through automated management tools.
Components of Cloud Computing
Frontend Platform
The cloud computing frontend consists of client-side interfaces such as web browsers or mobile apps, for example, that users utilize to interact with cloud services. These user-friendly interfaces enable interaction with resources, applications, and data in the cloud. For instance, a web-based dashboard allows users to monitor their cloud infrastructure, deploy applications, and manage storage. Mobile apps provide similar functionalities, enabling users to access cloud services on the go. Cloud technologies facilitate a seamless user experience for businesses, making the frontend platform critical in this context.
Invest in Professional UX/UI Design to Create Impactful Interfaces
Designing Seamless User Journeys That Boost Interaction and Conversion Rates
Discover UI/UX DesignBackend Platform
The backend platform is the backbone of cloud computing, consisting of servers, storage systems, and virtualization technology that manage data and applications. Servers provide the necessary computing power to run applications and perform complex computations. The storage systems offer scalable and reliable data solutions. Virtualization technology optimizes resource use and reduces costs by allowing multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server. The backend platform ensures cloud services are reliable, scalable, and efficient, catering to various business needs.
Application Layer
The application layer processes requests made by users and delivers services and resources to them. This layer comprises many cloud-based applications and services, such as software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). SaaS consists of software applications delivered over the internet, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance. PaaS, on the other hand, provides a platform for developers to build and deliver their applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. A main feature of IaaS is the provision of virtualized computing resources, like virtual machines and storage, on a pay-as-you-go basis. At this layer, users have the right tools and services available to run their businesses efficiently.
Cloud Service Management
Cloud service management allocates services such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS based on user access. This component manages user accounts, permissions, and service subscriptions. It guarantees that users have the proper rights and that resources are distributed according to demand. Monitoring and optimizing resource usage to create cost efficiency and performance is part of managing cloud services. When businesses manage cloud services effectively, cloud computing can provide maximum benefits while allowing them to retain control of their IT environment.
Storage
Cloud storage offers flexible and scalable data storage solutions. Businesses can store large volumes of data without physical hardware using cloud storage. It enables on-demand access to data, allowing users to retrieve and manage their files from any location with an internet connection. Cloud storage solutions can scale according to users’ needs and adapt up or down as required. With this flexibility, businesses don’t need to worry about storage limitations when managing data growth. Additionally, cloud storage usually includes data redundancy and backup features, enhancing data reliability and security.
Infrastructure Layer
The infrastructure layer consists of the hardware and software components on which all cloud operations depend. This includes physical servers, networking equipment, data centers, and virtualization software. Cloud services rely on this infrastructure layer to ensure they are reliable, scalable, and secure. The physical hardware in data centers features state-of-the-art cooling, power, and security systems to optimize performance. Networking equipment allows servers to communicate and transfer data to users quickly and reliably. Virtualization software enables the creation of virtual machines and other virtual resources, making efficient use of hardware, so you can save money.
Security
A key concern in cloud computing is security, which involves protecting cloud resources and user data through encryption, access management, and firewalls. Encryption ensures that data is secure both in transit and at rest, making it inaccessible to unauthorized individuals. Access management governs who can access cloud resources and what actions they can perform with them. This includes enforcing strong authentication methods like MFA and determining whether users are internal or external, along with their roles and permissions. Firewalls provide an additional layer of protection, allowing you to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on your chosen security rules. Vulnerabilities are addressed, and industry standards are upheld through regular security audits and updates conducted by cloud providers.
Key Differences Between Edge and Cloud Computing
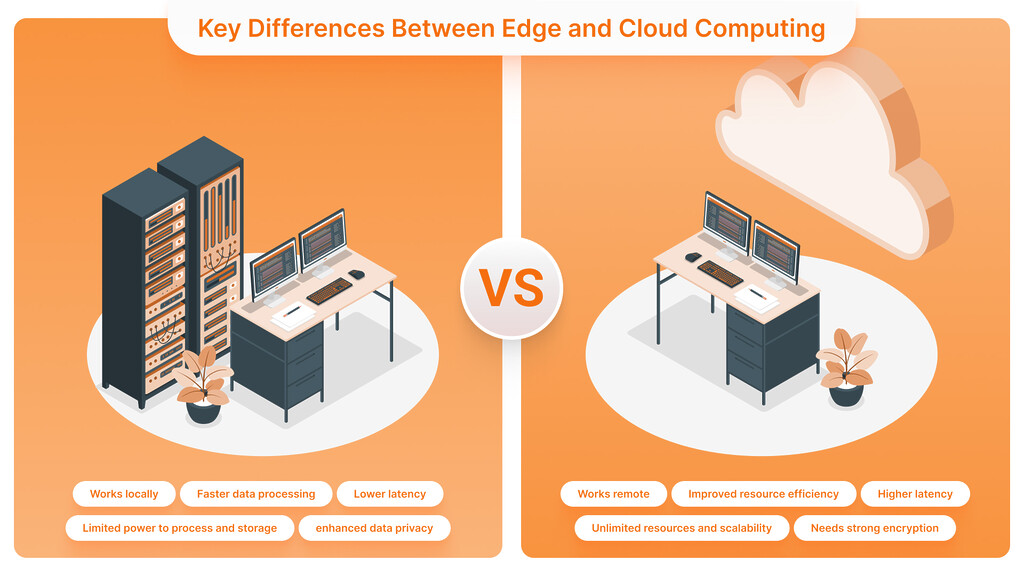
Data Processing Location
Edge Computing Works locally closer to the source of data generation using distributed computing nodes at the network edge. This eliminates the need to transfer large volumes of data to central servers, which allows for faster data processing and decision-making.
Cloud Computing does not process data but stores and processes it in centralized remote data centers using a network of remote servers. This approach improves resource management efficiency and scalability but introduces latency due to the distances involved in data transfer.
Latency and Response Time
Edge Computing offers lower latency because of local processing and is suitable for real-time applications requiring immediate response. It processes data near its source, helping applications make quick decisions and perform better with latency-sensitive applications.
Cloud Computing: Data may have further latency due to the distances it must travel to reach centralized data centers. Although cloud computing offers very high performance, it is better suited to applications where latency requirements are not rigid and some delay in data processing can be tolerated.
Scalability and Resources
Edge Computing has limited power to process and storage capacity due to its dependency on distributed nodes at the network edge. Deploying additional resources at the edge can be complex and resource-intensive, thus scaling edge computing.
Cloud Computing: It offers virtually unlimited resources and scalability and can be scaled up or down very quickly as per the demand. The infrastructure is managed by cloud providers, simplifying scaling without requiring significant upfront investment in hardware.
Data Security and Privacy
Edge Computing: Processing data locally enhances data privacy and reduces the attack surface by reducing the amount of data that has to be transferred. Yet, edge devices might be exposed to a physical attack, making it necessary to ensure their robust security.
CloudComputingoffers robust centralized security to data stored in far-flung data centers through encryption, access controls, and routine security upgrades. However, data transmission on the Internet may create security issues, so it must be transmitted with strong encryption and secure communication protocols.
Architectural Differences
Businesses need to understand the architectural differences between edge computing and cloud computing to determine which model best meets their architectural needs.
Edge Computing Architecture
Decentralized Nodes: The concept is simple. In the world of edge computing, computation happens on a device or a local server rather than a central data center. Strategically placed decentralized nodes are near the data source so the data can be processed quicker and doesn’t have to travel so far.
Proximity to Data Source: Edge computing processes data near its source, significantly reducing latency and bandwidth usage. This proximity allows data to be processed and analyzed almost instantly, making it perfect for applications that require real-time response, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
Local Data Handling: Edge computing encloses data, improving data privacy and security. This approach is in contrast to the one described above, which minimizes the risk of data breaches by minimizing any sensitive information transferred over the Internet. Local data processing also enables decision-making and immediate action, which is indispensable for time-sensitive applications.
Cloud Computing Architecture
Centralized Servers: Cloud computing uses centralized servers in large, remote data centers. Cloud service providers own these data centers, which house immense amounts of computational power and storage capacity. Centralized processing allows for efficient resource management and scalability.
Internet Dependency: For cloud computing to be realized, data transmission between users and remote data centers depends on network connectivity. This improves global accessibility and collaboration but also increases the possibility of latency and reliability, particularly in internet-unfavourable regions.
Scalable Resources: Perhaps one of cloud computing’s biggest strengths is its ability to power large-scale processing and storage requirements. Cloud providers offer virtually unlimited scalability, which businesses can use to scale resources as needed. Most importantly, this scalability is good for applications with fluctuating demand, such as e-commerce platforms and data analytics.
Digital Transformation for Competitive Advantage
Empowering Your Business with Tailored Digital Solutions
Explore Digital TransformationIndustries Benefiting from Edge Computing
Manufacturing (Industry 4.0)
Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing machine performance data in real time, manufacturers can predict equipment failures before they occur. This proactive approach reduces downtime, extends the life of machinery, and lowers maintenance costs.
Process Quality Improvement: In edge computing, data is processed locally to improve decision-making and data analysis quality. The outputs are therefore of higher quality. Manufacturers can, therefore, quickly detect and resolve production issues, resulting in consistent product quality.
Flexible Production: Edge computing supports mobile manufacturing setups and reduces setup times. This flexibility enables manufacturers to respond quickly to fluctuations in production demand and manage operations that are as efficient and cost-effective as possible.
Healthcare
Patient Monitoring: Edge-enabled wearable devices can monitor patient health metrics in real time. Continuous monitoring improves patient care, allowing us to intervene on time and personalize treatment plans.
Remote Diagnostics: In critical situations, edge computing allows for faster processing of medical imaging and diagnostics. By analyzing data locally, healthcare providers can diagnose patients more quickly and accurately.
Tailored Mobile Solutions for Your Unique Needs
Redefine Your Business with Mobile Application Development
Explore Mobile App DevelopmentRetail
Personalized Shopping: With edge computing, retailers can analyze customer behaviour in real time and tailor promotions and shopping experiences that are personalized. This makes customers happy and increases sales.
Inventory Management: Restocking and price adjustment happen in real time, as inventory data is instantly processed. This allows retailers to maintain the optimal stock level, avoid waste, and respond flexibly to market needs.
Energy Sector
Equipment Monitoring: Edge computing supports predictive maintenance for power plants and wind farms, allowing for real-time analysis of equipment performance data. This proactive maintenance approach benefits minimal downtime and maximum energy production efficiency.
Energy Distribution Optimization: Edge computing analyzes usage data locally to optimize energy distribution. This ensures that energy is delivered without waste and, therefore, with lower operational costs.
Transportation and Logistics
Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing is needed for the real-time data processing demanded by autonomous vehicles. The sheer amount of data these vehicles produce is overwhelming, and it needs to be processed in real time so that the vehicles can operate safely and efficiently.
FleetManagement: Edge computing allows for real-time tracking of goods and vehicle conditions. It enhances fleet management by improving routes, decreasing fuel usage, and guaranteeing on-time deliveries.
Scenarios Where Cloud Computing Is the Better Choice
Large-Scale Data Processing and Analytics
Cloud computing is an ideal solution for businesses dealing with huge amounts of data, providing almost infinite scalability at minimal capital investment. Cloud platforms can be useful to companies working in big data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence by helping them process and analyze large datasets efficiently. Cloud providers provide businesses with powerful computing resources and advanced analytics tools to help them make insightful decisions and derive value from their data.
Fluctuating Workloads
Variable computing business needs are enabled by the ability to scale resources in cloud computing quickly. This flexibility is perfect for:
- E-commerce Platforms during Peak Seasons: Online retailers can improve their infrastructure to cope with a rise in traffic during holiday sales or promotion activity and guarantee that customers always enjoy a seamless shopping experience.
- Media Streaming Services during Popular Events: With the ability to scale resources, streaming platforms can support spikes in viewership during big events like sports championships or new movie releases.
- Startups Experiencing Rapid Growth: Rapid user growth and expanding operations can be scaled quickly with negligible investment in hardware for startups.
Global Reach and Collaboration
With data and applications available in the Cloud, remote work and global collaboration have become a reality—all that is needed to access them is an internet connection. This is especially useful for a multinational company or a distributed team. They can collaborate in real time, share documents, and even access critical business applications from anywhere. Both Microsoft Teams and Google Workspace are cloud collaboration tools that improve productivity and streamline communication.
Cost-Sensitive Operations
Cloud computing is one of the best ways for businesses to avoid upfront capital expenditures by switching to a pay-as-you-go model. With the cloud, there is no need to spend excess money on maintenance and upgrades; cloud providers take care of infrastructure management, security updates, and hardware replacements. This helps businesses control their budgets conveniently, putting aside money for strategic initiatives rather than IT infrastructure.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Geographically distributed data centers deliver robust disaster recovery and business continuity solutions through the cloud. When a natural disaster, cyber attack, or system failure occurs, businesses can recover lost data and return to normal operations in little to no time. Cloud providers provide automated backup and recovery, ensuring that critical data are protected and accessible at all times. Therefore, maintaining business continuity and protecting against data loss is crucial to resilience.
Successful Implementations

Edge Computing Examples
Autonomous Vehicles
For example, edge computing helps companies like Uber make real-time decisions in autonomous vehicles. These vehicles can quickly analyze their surroundings using data from sensors and cameras processed locally, making split-second decisions to navigate safely. Local processing can only guarantee the responsiveness and reliability necessary for autonomous driving.
Healthcare
Hospitals use edge computing to analyze data in real-time better and offer better patient care. Patient data is collected by wearable devices and medical sensors and processed locally to deliver real-time insights. This allows healthcare providers to continuously monitor patients, detect anomalies quickly, and address them in time, leading to better patient outcomes.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, edge computing is used for real-time process optimization and predictive maintenance. Sensors collect performance data on machinery, which is then analyzed locally to determine inefficiencies and predict possible failures. By taking a proactive approach, downtime is greatly reduced, equipment life is extended, and production quality is improved.
Retail
Retailers are harnessing edge computing to analyze in-store customer behavior in real time. By processing data from cameras and sensors locally, retailers can see customer shopping patterns and preferences. This information is employed to create personalized shopping experiences, optimize store layouts, improve inventory management, and ultimately drive sales and customer satisfaction.
Cloud Computing Examples
Netflix
Amazon Web Services (AWS) powers Netflix’s streaming service, which scales globally. Thanks to the scalable infrastructure available with AWS, Netflix can store vast amounts of data and stream high-quality content to millions of users around the world. Netflix relies on the cloud platform to deploy new features quickly, optimize content delivery, and provide a seamless viewing experience.
Airbnb
Cloud Computing with AWS helps Airbnb manage its platform efficiently by allowing it to operate globally. Thanks to the cloud infrastructure, Airbnb can scale resources only when needed, allowing the platform to remain responsive and reliable even during peak booking periods. Airbnb’s flexibility to deliver the user experience and grow its services has never been greater.
Capital One
Through migration to the cloud and adoption of AWS, Capital One modernized its IT infrastructure to accelerate product development and innovation. The cloud platform delivers the agility and scalability needed to develop and deploy new financial products quickly. Using cloud services, Capital One can strengthen security, enhance customer experience, and compete in the financial industry.
General Electric (GE)
General Electric (GE) performs data consolidation and analytics using Microsoft Azure. By migrating its data to the cloud, GE can centralize information from various sources and conduct advanced analytics. GE utilizes Azure’s powerful analytics tools to optimize operations, make informed decisions, and foster innovation across its business units.
Hybrid Approach: Combining Edge and Cloud Computing
A hybrid edge cloud model can combine edge and cloud computing, leveraging each attribute while building a more efficient, flexible IT infrastructure. This approach leverages the low latency and real-time processing of the edge and the scalability and resources of the cloud.
Experience Our Research & Development Expertise
R&D-Led Software Development Integrates Innovation into Every Product Detail
Learn About R&D ServicesOptimized Performance
A hybrid edge-cloud model performs computations at the edge for processes that require immediate operation, while sending data-intensive tasks or complex processes to the cloud. For instance, edge devices can quickly analyze and respond to real-time sensor and camera data, such as making a swift decision to open a door. In contrast, the cloud is equipped to manage more intricate analytics, machine learning models, and long-term data storage. This division of labor ensures that each task is conducted in the most suitable environment, maximizing efficiency performance.
Flexibility
The hybrid approach provides flexibility to tweak the infrastructure needs of businesses based on their requirements. Organizations can deploy edge devices to perform local calculations, and cloud resources can be used for tasks that require a lot of computational work or storage. The versatility of this architecture allows companies to stretch the fabric of their infrastructure to match the needs of any workload or shifting needs without overloading any single part of it.
Enhanced Security
Processing sensitive data locally at the edge is more secure because it removes a lot of data from the Internet. It reduces the risk of data breach during transmission and ensures sensitive information stays within a confined environment. However, robust centralized security measures offered by cloud service providers can still be utilized to store sensitive tasks in the cloud or to use the cloud for less sensitive tasks and long-term storage.
Reduced Latency
By processing locally at the edge, delays are minimized, enabling local applications to achieve real-time responsiveness. Businesses can ensure quick decision-making and actions since time-sensitive tasks are handled at the edge. Meanwhile, less time-sensitive tasks, such as data aggregation, analysis, and storage, can be managed in the cloud manage.
Real-World Applications
Autonomous Vehicles
Edge computing in autonomous vehicles supports most real-time functions, such as obstacle detection, navigation, and quick decision-making. Meanwhile, the cloud handles software updates, long-term data storage, and advanced analytics. The advantage of this hybrid approach is that autonomous vehicles can continually improve with cloud updates and insights without sacrificing safety efficiency.
Smart Cities
Smart cities use edge computing to control real-time traffic lights, environmental sensors, and public safety systems. By aggregating data from a myriad of sources and offering long-term urban development insights, the cloud supports city-wide planning and analysis. This combination makes smart city initiatives more efficient and responsive.
Manufacturing
Edge Computing in manufacturing is used for machine control, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance. Factory floor data is immediately processed at the edge and applied to the factory floor to make immediate adjustments and optimizations. Manufacturers use the cloud for data storage, advanced analytics, and long-term planning to improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve product quality.
Data Privacy and Security Considerations
Edge Computing
Challenges:
- Decentralized Environment: Unlike centralized cloud infrastructure, edge computing is decentralized, which increases risk because of more diverse and less secure processing locations. These edge devices must process data locally, so ensuring that the same level of security is maintained on each device is tough.
- Device Vulnerability: Many edge devices may exhibit inconsistent security standards, leading to vulnerabilities. Different devices can implement varying security measures robustly, making them differentially vulnerable to attack.
- Data Interception Risks: Such devices may include smaller edge devices, such as sensors and IoT gadgets, that are more vulnerable to unauthorized access and data interception. However, these devices usually do not have the same levels of security as more centralized, larger systems.
Security Measures:
- Encryption protects data at rest and in transit. If data is intercepted, it will be unreadable to anyone who shouldn’t have access to it.
- Access Controls: Strict authentication protocols and access controls are necessary to secure edge devices. These encompass multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict access to sensitive data.
- Data Governance: Having robust data governance policies helps align with the privacy regulations & standards. This encompasses everything from audits regularly to data classification and sticking to industry-specific regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
Cloud Computing
Challenges:
- Centralized Storage Risks: The cloud’s legacy of being based on centralized data storage makes attacks possible. If your data repositories are large, malicious actors will come sniffing around, looking to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Shared Responsibility: In cloud computing, the cloud provider and customer divide the security responsibilities. Although providers are responsible for securing the cloud infrastructure, customers are responsible for securing their data and applications in the cloud.
Security Measures:
- Encryption and Tokenization: Data is secured by encrypting it and tokenizing it. These ensure that sensitive data remains secure at all times, whether in storage or during transmission.
- Access Control Systems: Strict access protocols, such as MFA and RBAC, can help restrict access to cloud resources. These systems ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data and applications.
- Monitoring and Auditing: They continuously monitor and audit your cloud environments to detect anomalies and prevent unauthorized activities. Tools and services help cloud providers with real-time monitoring, threat detection, and compliance report preparation.
Conclusion: Which Is Right for Your Business?
Whether you need to meet a business requirement or have business goals, you should decide whether to use edge computing or cloud computing. Each model has advantages that may profoundly affect your operations and strategic goals.
- If your applications need real-time data processing, low latency, and enhanced privacy, choose EdgeComputing. This model works well for industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and autonomous vehicles, where real-time data analysis and fast decision-making are needed. Edge computing allows data to be processed locally for faster response times and greater data security.
- Choose Cloud Computing if you want scalability, cost efficiency, and global accessibility. It is an excellent fit for businesses undertaking large-scale data analytics, dealing with fluctuating workloads, or needing to deploy applications and services quickly. Its pay-as-you-go model and virtually unlimited resources make scaling operations easy and cost-effective.
- If you wish to benefit from both models, consider a Hybrid Approach. Edge and cloud computing can be combined for the best performance, maximum security, and better flexibility. With this approach, you can perform time-sensitive processing locally and then utilize the cloud for complex computations, data storage, and long-term analytics. A hybrid model is an advantage since you can easily adjust to changing business needs and still get the best of both worlds.
Through a thorough evaluation of your business needs and an explicit knowledge of each model’s strengths and weaknesses, you can make an intelligent, fit-for-purpose choice that supports your strategic goals and sets your business up for success.
Contact us if you need guidance in making the best decision for your business!